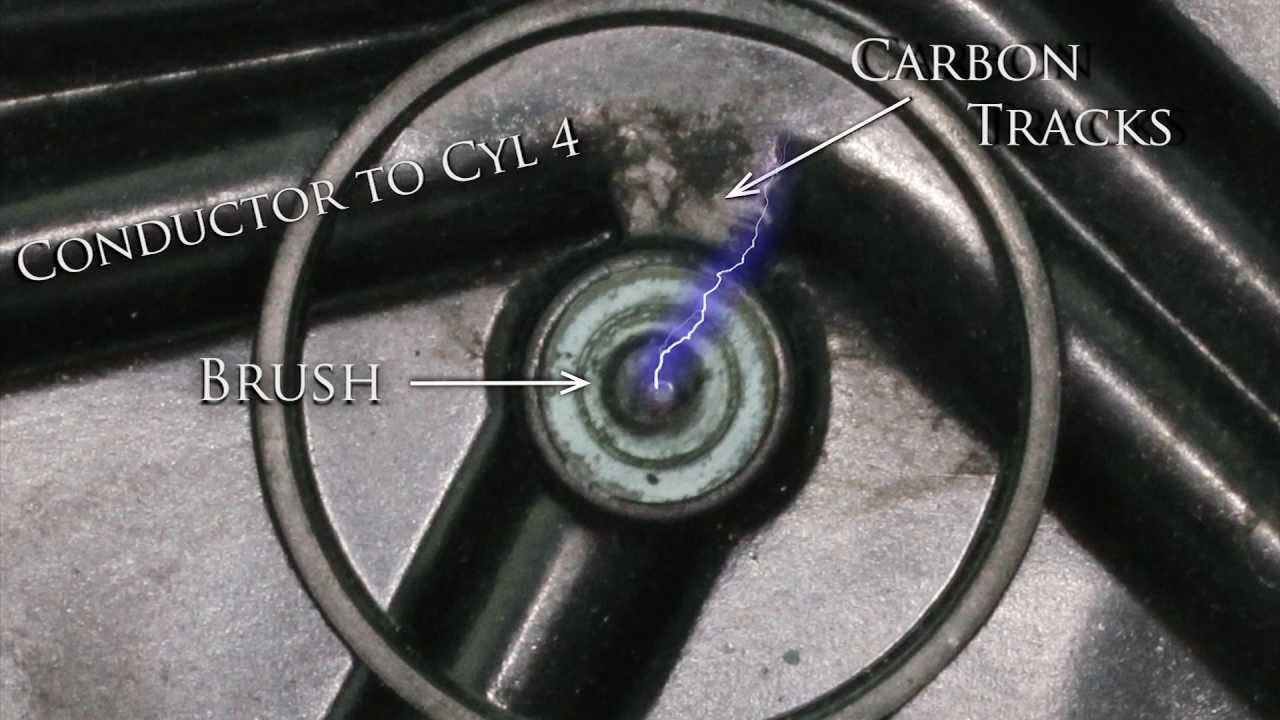
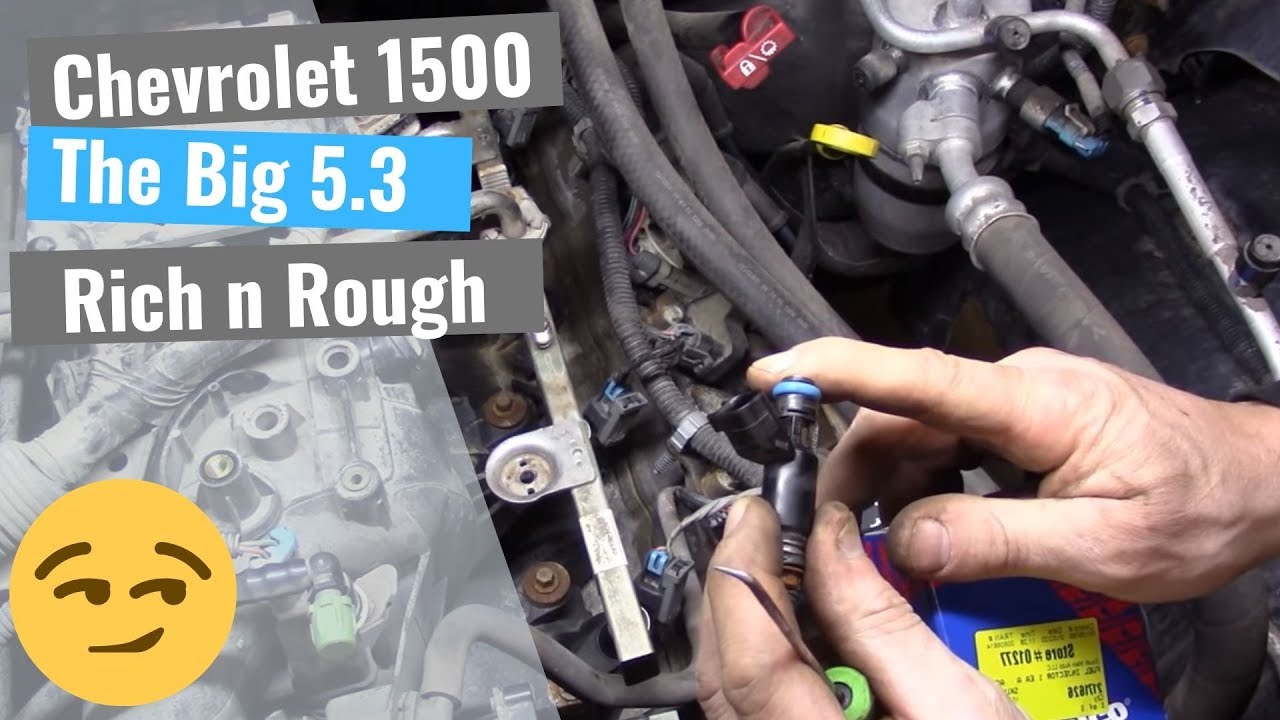
Experiencing rough idling, reduced power, or a flashing check engine light in your GMC? The culprit could be lurking within your engine's combustion chambers. One common issue that plagues GMC owners is the dreaded P0300 engine code, signifying random misfires. This article dives deep into the world of the P0300 code, helping you understand its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
The P0300 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic OBD-II code, meaning it applies to a wide range of vehicles, including GMC trucks and SUVs. This code specifically indicates that the engine control module (ECM) has detected random misfires across multiple cylinders. Unlike codes like P0301 (misfire cylinder 1) or P0302 (misfire cylinder 2), the P0300 code doesn't pinpoint a specific cylinder. This makes diagnosing the root cause a bit more challenging, requiring a more systematic approach.
The OBD-II standard, introduced in the mid-1990s, revolutionized vehicle diagnostics. The standardization of diagnostic trouble codes like P0300 made it easier for mechanics to identify and address engine problems across different makes and models. Before OBD-II, diagnosing engine issues was often a time-consuming and costly process. The P0300 code itself has been a part of the OBD-II standard since its inception, helping countless GMC owners address random misfire issues.
Understanding the P0300 code is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your GMC engine. Ignoring this code can lead to more severe problems, such as catalytic converter damage, decreased fuel economy, and increased emissions. Addressing the underlying issue promptly can prevent costly repairs down the road and ensure your GMC continues to run smoothly.
Several factors can trigger a P0300 code in your GMC. These range from relatively simple issues like worn spark plugs or faulty ignition coils to more complex problems like vacuum leaks, fuel delivery problems, or even internal engine damage. The diagnostic process often involves a combination of visual inspections, component testing, and specialized diagnostic tools.
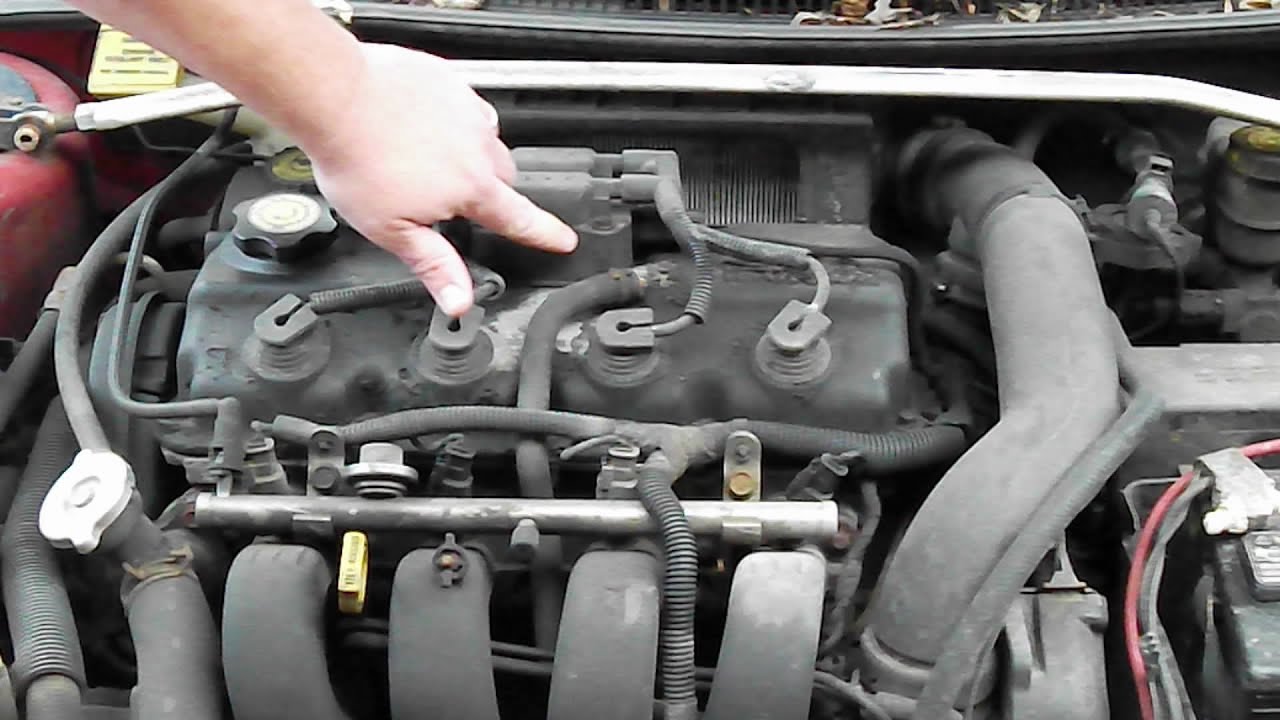
Common causes of the P0300 code include: faulty spark plugs or wires, malfunctioning ignition coils, vacuum leaks in the intake manifold or hoses, low fuel pressure, clogged fuel injectors, a problematic mass airflow sensor, a defective oxygen sensor, and issues with the EGR valve. More severe causes, though less frequent, might include problems with the camshaft sensor, crankshaft sensor, or even internal engine damage like worn piston rings or valves.
Diagnosing P0300 involves checking for damaged spark plugs or wires, testing ignition coils, looking for vacuum leaks, checking fuel pressure and injectors, inspecting the mass airflow sensor and oxygen sensors, and examining the EGR valve. Advanced diagnostics might involve analyzing camshaft and crankshaft sensor data or performing a compression test to identify internal engine issues.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Early P0300 Code Diagnosis
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Prevents further engine damage | Can require specialized diagnostic tools |
| Improves fuel economy | May involve some trial and error |
| Reduces harmful emissions | Can be time-consuming |
Frequently Asked Questions about P0300:
1. What does P0300 mean? A: P0300 indicates random multiple cylinder misfires.
2. What causes P0300? A: Several factors, including faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, vacuum leaks, fuel delivery issues, etc.
3. How do I fix P0300? A: Diagnosis is essential. Start with the simpler checks like spark plugs and work towards more complex ones.
4. Can I drive with a P0300 code? A: It's not recommended. Continued driving can exacerbate the problem and cause further damage.
5. Is P0300 serious? A: Yes, it can be. Ignoring it can lead to costly repairs.
6. How much does it cost to fix P0300? A: The cost varies depending on the underlying cause.
7. How can I prevent P0300? A: Regular maintenance, including timely spark plug and ignition coil replacements, can help prevent this code.
8. Can bad gas cause P0300? A: Yes, contaminated or low-quality fuel can contribute to misfires.
Tips for dealing with a P0300 code: Keep a record of any other symptoms occurring alongside the P0300 code. Consult a reliable mechanic experienced with GMC vehicles. Use quality fuel and perform regular maintenance. Don’t delay diagnosis and repair to prevent further damage.
In conclusion, the GMC engine code P0300 signifies a random misfire issue that demands attention. Understanding the potential causes, diagnostic steps, and possible solutions can empower you to address this problem effectively. While a P0300 code can seem daunting, a systematic approach, combined with regular maintenance, can help prevent misfires and keep your GMC running smoothly. Don't ignore that check engine light – address it promptly to avoid more serious problems down the road. By understanding and addressing this code, you can ensure optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity for your GMC engine. Addressing the P0300 code promptly will save you money and headaches in the long run.
P601 Error Code Chevy Silverado Forum - Trees By Bike
gmc engine code p0300 - Trees By Bike
gmc engine code p0300 - Trees By Bike
Gmc Engine Code P0300 - Trees By Bike
Code P0300 Check Engine Light - Trees By Bike
Po304 Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected - Trees By Bike
gmc engine code p0300 - Trees By Bike
Toyota 4runner Check Engine Light Code P0300 - Trees By Bike
Chevy Engine Code P0300 - Trees By Bike
gmc engine code p0300 - Trees By Bike
gmc engine code p0300 - Trees By Bike
Gmc Engine Code P0300 - Trees By Bike
Random Misfire Code P0300 - Trees By Bike
gmc engine code p0300 - Trees By Bike
Chevy Engine Code P0300 - Trees By Bike