Have you ever opened your electricity bill and felt a jolt of surprise? You're not alone. Fluctuating energy costs are a common concern, and understanding how price caps on electricity rates per kilowatt-hour (kWh) work can feel like deciphering a secret code. This article aims to shed light on the often-confusing world of kWh price limitations, empowering you to navigate your energy bills with confidence.
Electricity price caps per kWh are essentially limits placed on how much energy suppliers can charge you for each unit of electricity you consume. These caps can be implemented by governments or regulatory bodies to protect consumers from excessive price hikes. They can be influenced by a variety of factors, from global energy market trends to local regulations. Understanding these influences is crucial to understanding the dynamics of your electricity bill.
The history of electricity price regulation is a complex one, often evolving in response to market instability or consumer advocacy. Early forms of regulation focused on ensuring fair access to electricity, while more recent approaches have incorporated environmental concerns and the promotion of renewable energy sources. The implementation of kWh price caps represents a shift towards more direct consumer protection, aiming to provide a degree of predictability and affordability in the energy market.
The importance of electricity price caps per kWh lies in their potential to shield consumers from volatile energy markets. Without these safeguards, households and businesses could face unpredictable and potentially unaffordable energy bills. Price caps offer a level of stability, allowing for better budgeting and financial planning. However, the effectiveness of these caps depends on careful implementation and ongoing monitoring to ensure they truly benefit consumers.
A key issue surrounding electricity price caps is the balance between consumer protection and market competition. While caps can protect consumers from price gouging, excessively restrictive caps could discourage investment in the energy sector and limit innovation. Finding the right balance is a continuous challenge, requiring careful consideration of both consumer needs and market dynamics.
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is the standard unit of measurement for electricity consumption. One kilowatt-hour is equivalent to using 1,000 watts of electricity for one hour. For example, if you run a 100-watt light bulb for 10 hours, you've used one kWh of electricity.
One benefit of kWh price caps is increased price transparency. By setting a limit on the per-unit cost, consumers have a clearer understanding of their potential energy expenses. Another benefit is enhanced consumer protection against unreasonable price increases. This can be especially helpful during periods of market volatility. Finally, price caps can promote energy efficiency by encouraging consumers to be mindful of their electricity usage, knowing that exceeding a certain consumption level could lead to higher costs even with the cap in place.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electricity Price Caps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Consumer protection from high prices | Potential disincentive for energy investment |
| Increased price transparency | Possible reduction in market competition |
| Promotion of energy efficiency | Risk of supply shortages if caps are too low |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a kWh price cap? - A limit on the amount suppliers can charge per unit of electricity.
2. Who sets these caps? - Typically, government regulatory bodies.
3. How are caps determined? - Factors include market conditions, production costs, and consumer needs.
4. Do caps always apply? - Not always; some markets operate without price caps.
5. Can caps change? - Yes, they can be adjusted based on market fluctuations.
6. How do I find out the current cap in my area? - Contact your local energy regulator or supplier.
7. What happens if prices exceed the cap? - Suppliers cannot legally charge above the established cap.
8. Are there penalties for suppliers who violate the cap? - Yes, regulators can impose fines and other penalties.
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of electricity pricing can be challenging. However, understanding the concept and implications of kWh price caps is a crucial step towards taking control of your energy bills. These caps play a vital role in protecting consumers from price volatility, promoting transparency, and encouraging responsible energy consumption. By staying informed about current electricity prices per kWh cap and their impact on your energy costs, you can make informed decisions and potentially save money on your electricity bills. Take the time to research your local regulations, compare supplier offerings, and consider implementing energy-saving practices to maximize the benefits of price caps. Your wallet and the planet will thank you.
UK electricity prices per kWh - Trees By Bike
current electricity prices per kwh cap - Trees By Bike
Chart The UK Energy Price Cap Is Through the Roof - Trees By Bike
History of Ofgems Energy Price Cap Per kWh UK Future Estimates - Trees By Bike
50 best ideas for coloring - Trees By Bike
Ten trends in global and Philippine energy - Trees By Bike
Gas And Electric Prices 2024 Uk - Trees By Bike
How Much Electricity Does A House Cost Per Day Uk at Joshua Driggers blog - Trees By Bike
Average Household Electricity Consumption - Trees By Bike
Electricity Price Uae at Lai Morin blog - Trees By Bike
Electricity and gas prices in the first half of 2022 - Trees By Bike
current electricity prices per kwh cap - Trees By Bike
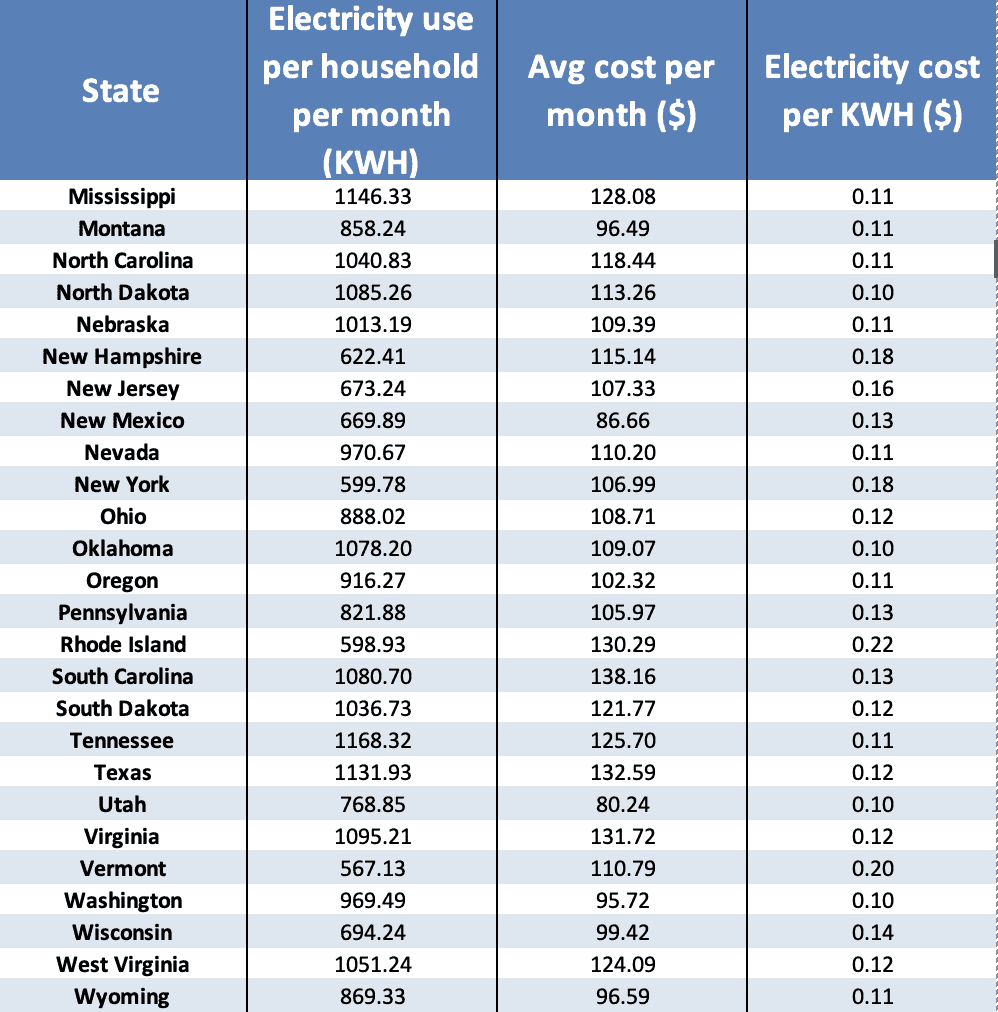
Cost Of Electricity Per Kwh By State 2025 - Trees By Bike
Electricity Prices Uk at Peter Berke blog - Trees By Bike
Average Electricity Prices in kWh - Trees By Bike