Are you feeling the energetic hum of rising utility bills? You're not alone. Understanding the nuances of energy price caps per kilowatt-hour (kWh) is crucial for navigating the ever-shifting landscape of household expenses. Let's dive into the world of regulated energy costs and discover how to harmonize your consumption with conscious spending.
Energy price caps, like a gentle hand on the reins of runaway costs, are government-imposed limits on the maximum amount energy suppliers can charge per unit of gas or electricity, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). These caps aim to protect consumers from exorbitant price hikes, fostering a sense of financial stability in an otherwise volatile market. Imagine them as a shield, deflecting the full force of market fluctuations.
The origins of energy price caps can be traced back to periods of market instability, where unchecked price surges threatened to leave households struggling to afford essential utilities. These regulations, though sometimes complex, provide a framework for ensuring fair pricing. Think of them as a balancing act, weighing the needs of consumers against the realities of the energy market.
The importance of understanding gas and electricity price caps per kWh cannot be overstated. These caps directly impact your monthly energy bills, influencing your budget and overall financial well-being. By grasping the mechanics of these regulations, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your energy consumption. This knowledge is like a key, unlocking the door to greater control over your energy expenses.
However, energy price caps are not without their complexities. One key issue revolves around the balance between protecting consumers and ensuring a viable market for energy suppliers. Setting caps too low can discourage investment in renewable energy sources and infrastructure upgrades, while setting them too high leaves consumers vulnerable to price volatility. It's a delicate dance, requiring careful consideration of various factors.
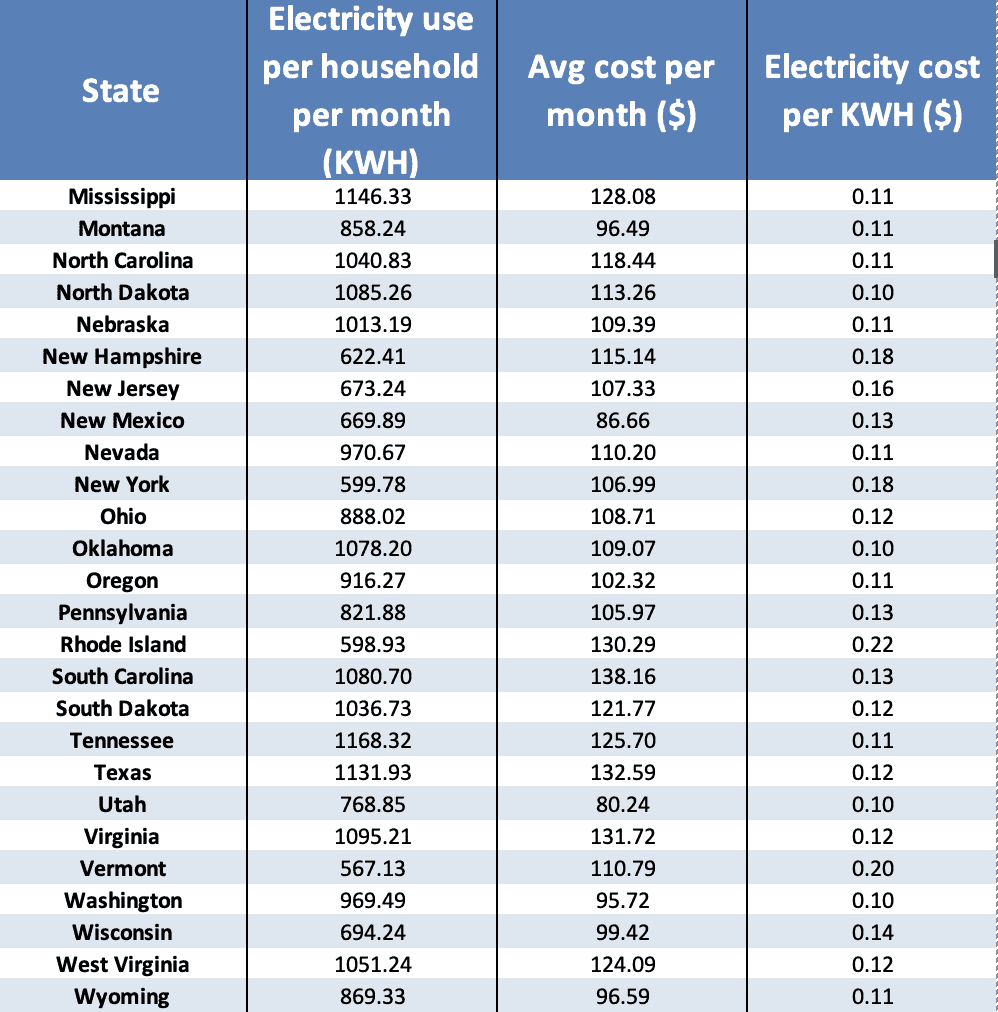
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a standard unit of energy measurement. It represents the amount of energy used by a 1,000-watt appliance for one hour. For instance, a 100-watt light bulb running for 10 hours consumes 1 kWh of electricity.
One benefit of price caps is predictable budgeting. Knowing the maximum you'll pay per kWh allows for more accurate financial planning. Another advantage is consumer protection. Price caps shield households from extreme price fluctuations, particularly during periods of market volatility. Finally, they promote market stability by preventing excessive price hikes that could destabilize the energy sector.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Energy Price Caps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable Budgeting | Potential Disincentive for Investment |
| Consumer Protection | Possible Supply Shortages |
| Market Stability | Administrative Complexity |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a kWh? A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a standard unit of energy measurement.
2. How are price caps determined? They are typically set by regulatory bodies based on market analysis.
3. Do price caps apply to all energy suppliers? This varies depending on local regulations.
4. How often are price caps reviewed? Review frequency varies depending on the regulatory framework.
5. Can I switch energy suppliers even with price caps in place? Yes, competition is often still encouraged within the capped pricing structure.
6. Are there different price caps for different times of day? Time-of-use tariffs may exist alongside price caps.
7. What happens if an energy supplier breaches the price cap? Penalties and enforcement actions are typically taken by regulatory bodies.
8. How can I monitor my energy usage? Smart meters and energy monitoring apps can help track consumption.
Tips for managing your energy consumption under price caps: Use energy-efficient appliances, monitor your usage, and consider time-of-use tariffs.
In conclusion, understanding gas and electric price caps per kWh is essential for navigating the complexities of today's energy market. These regulations serve as a vital tool for consumer protection and market stability, ensuring that essential utilities remain affordable. By grasping the intricacies of price caps, consumers can empower themselves to make informed decisions about their energy consumption and budget effectively. While challenges remain, the benefits of price caps contribute significantly to a more equitable and sustainable energy landscape. Take the time to research your local regulations, monitor your energy usage, and embrace energy-efficient practices. Empower yourself to make conscious choices that benefit both your wallet and the planet.
History of Ofgems Energy Price Cap Per kWh UK Future Estimates - Trees By Bike
Average Electricity Prices in kWh - Trees By Bike
Consumers Energy Cost Per Kwh 2024 - Trees By Bike
First Energy Rates Increase 2024 - Trees By Bike
Energy prices from January - Trees By Bike
Average Household Electricity Consumption - Trees By Bike
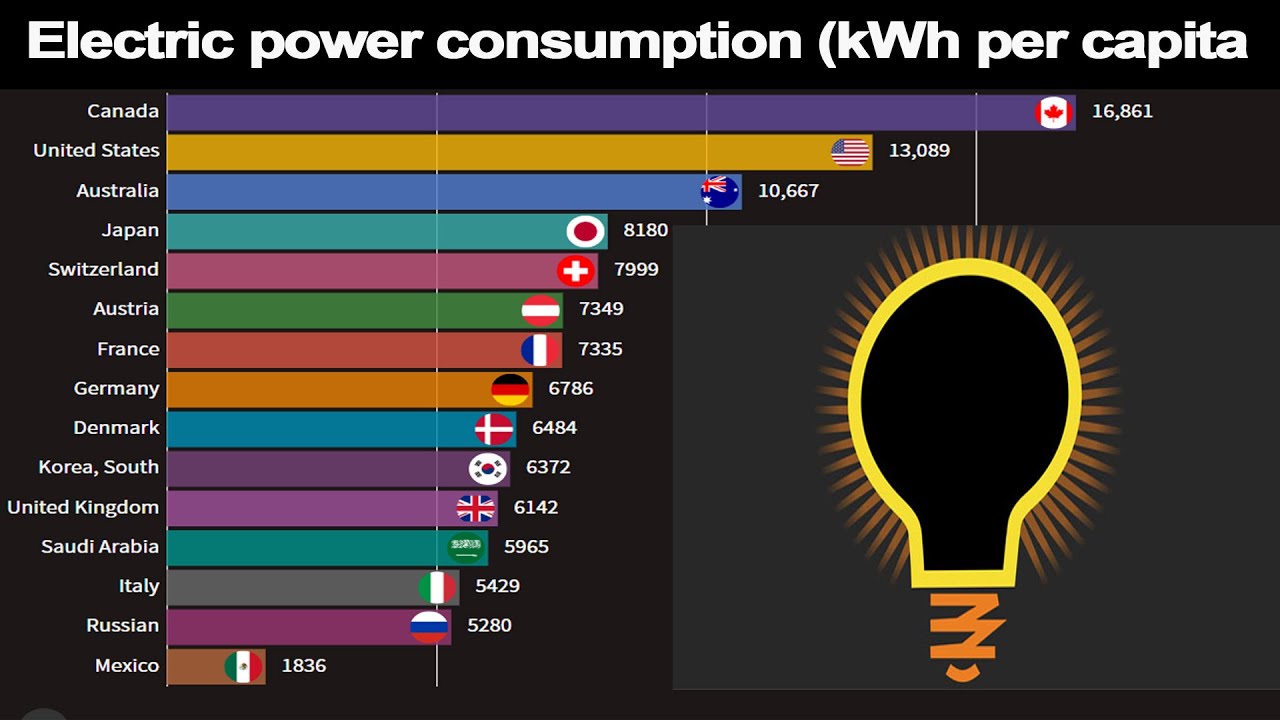
How Much Power Does The World Consume at Dave Eckert blog - Trees By Bike
Energy Price Cap Forecast 2024 Uk - Trees By Bike
Is Gas More Expensive Than Electricity Uk at Dolores Ferguson blog - Trees By Bike
Gas And Electric Prices 2024 Uk - Trees By Bike
gas and electric price cap per kwh - Trees By Bike
Guide to solar and increasing energy prices - Trees By Bike
What is the new energy price cap per kWh How the Ofgem rate works and - Trees By Bike
Countries seeing largest increase in electric and gas bills - Trees By Bike
gas and electric price cap per kwh - Trees By Bike