That dreaded check engine light has illuminated your dashboard, and your GM vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system (OBD-II) has reported the cryptic code: P0332. What does it mean? This frustrating situation is likely due to a problem with your crankshaft position sensor (CKP) circuit – specifically, low input. Understanding this code is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and preventing further damage.
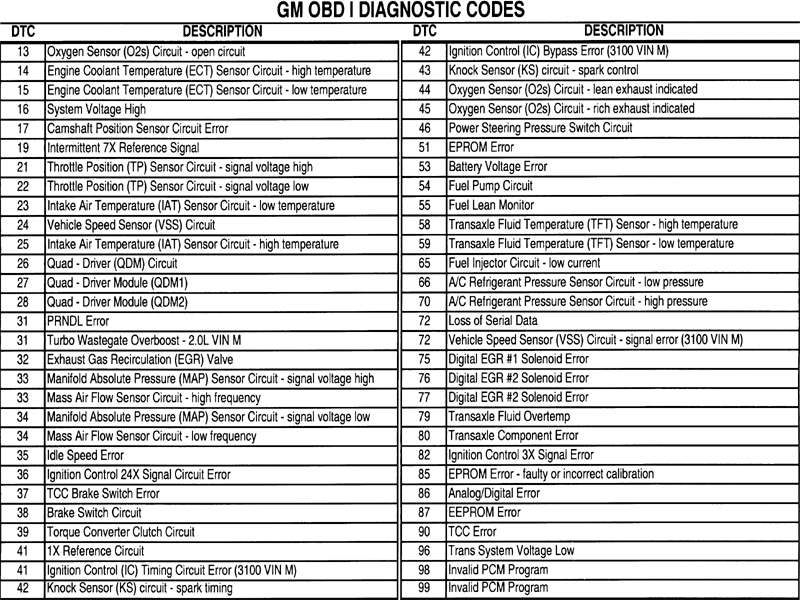
The P0332 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) specifically points to a low input signal from the crankshaft position sensor circuit. This sensor is a vital component of your engine management system. It monitors the rotational speed and position of the crankshaft, relaying this information to the engine control module (ECM). This data is essential for precise control of fuel injection and ignition timing. A faulty signal can lead to a variety of performance issues.
The crankshaft position sensor circuit in GM vehicles, like in most modern vehicles, has evolved over time with advancements in engine technology. The P0332 code itself is a standardized OBD-II code, meaning its interpretation remains consistent across various GM models. However, the specific location and configuration of the crankshaft position sensor can vary depending on the engine type and vehicle model year. Historically, diagnosing these issues could be complex, but modern diagnostic tools have simplified the process.
The importance of the crankshaft position sensor and its associated circuit cannot be overstated. The ECM relies on accurate data from this sensor for optimal engine operation. Without a properly functioning CKP circuit, the ECM cannot effectively manage fuel delivery and ignition timing. This can result in reduced engine performance, rough idling, difficulty starting, or even a complete engine stall. Addressing the P0332 code promptly is essential to prevent these issues and ensure the longevity of your engine.
Several problems can trigger the P0332 code. A common culprit is a damaged or worn crankshaft position sensor. Wiring issues within the circuit, such as frayed or corroded wires, can also be responsible. Additionally, a damaged crankshaft position sensor reluctor wheel (the toothed wheel that the sensor monitors) or excessive crankshaft endplay can cause this issue. Understanding the potential causes is the first step toward effective troubleshooting.
A failing crankshaft position sensor can manifest in several ways. Intermittent starting problems are a common symptom. The engine might crank but struggle to start, or it might stall shortly after starting. Rough idling, where the engine runs unevenly at idle, can also indicate a CKP sensor problem. Decreased engine performance, including hesitation or lack of power, is another potential indicator. Diagnosing these symptoms accurately can often pinpoint the underlying issue.
While there aren't direct "benefits" to a P0332 code itself, resolving it brings several advantages. A properly functioning CKP circuit restores optimal engine performance, resulting in smoother operation and improved fuel efficiency. Addressing the underlying issue also prevents further damage to the engine and related components. Finally, resolving the code turns off that annoying check engine light, giving you peace of mind.
Troubleshooting a P0332 code involves a systematic approach. Start by visually inspecting the crankshaft position sensor and its wiring for any obvious damage. Check for loose connections, corrosion, or damaged wiring. If no visual issues are found, using a diagnostic scanner to monitor the CKP sensor signal can help identify the problem. A multimeter can be used to test the sensor's resistance and voltage. If the sensor is faulty, replacing it is usually the solution.
Several best practices can help avoid crankshaft position sensor issues. Regularly inspecting the sensor and its wiring for damage can prevent future problems. Ensuring proper engine grounding can also help prevent electrical interference with the CKP circuit. Using high-quality replacement parts when repairs are needed is crucial for long-term reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dealing with P0332
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Restored engine performance | Can be time-consuming to diagnose |
| Improved fuel efficiency | May require specialized tools |
| Prevents further engine damage | Can be costly if professional help is needed |
Frequently Asked Questions about P0332
Q: Can I drive with a P0332 code? A: It's not recommended. While you might be able to drive for a short distance, it can lead to further engine damage.
Q: How much does it cost to fix a P0332 code? A: The cost can vary depending on the specific repair needed.
Q: What tools do I need to diagnose a P0332 code? A: A diagnostic scanner and a multimeter are helpful tools.
Q: Is it difficult to replace a crankshaft position sensor? A: The difficulty varies depending on the vehicle and your mechanical skills.
Q: Can a bad battery cause a P0332 code? A: While unlikely, a very weak battery can sometimes cause sensor issues.
Q: How can I prevent future P0332 codes? A: Regular maintenance and inspections can help prevent this issue.
Q: What other codes are related to the P0332 code? A: Other codes related to the crankshaft position sensor circuit include P0335 and P0336.
Q: Where is the crankshaft position sensor located? A: The location varies depending on the vehicle, but it's typically near the crankshaft pulley or harmonic balancer.
In conclusion, the GM engine code P0332 signals a problem within your vehicle’s crankshaft position sensor circuit. This crucial sensor plays a vital role in engine management, and a faulty signal can lead to various performance issues. Understanding the code’s meaning, potential causes, and troubleshooting steps is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s health and preventing further damage. While diagnosing and fixing the problem might require some effort, addressing the issue promptly will restore optimal engine performance, improve fuel efficiency, and provide peace of mind. Don’t ignore that check engine light – take action and get your vehicle back on track.
I have a 2000 gmc sierra 4x4 with a 48 engineits sending a code of - Trees By Bike
Ford Engine Number Identification - Trees By Bike
Chevy Big Block Engine Codes - Trees By Bike
Chevrolet Trouble Codes List - Trees By Bike
Chevy Silverado Knock Sensor PO332 Code Wiring Diagram More - Trees By Bike
Ls Engine Code Chart - Trees By Bike
Chevy Engine Code Information - Trees By Bike
QA Troubleshooting P0332 Code on 2000 GMC Sierra 48 - Trees By Bike
Gm Engine Code Po332 - Trees By Bike
Dodge Dakota Check Engine Light Codes - Trees By Bike
How To Decode Chevy Engine Codes - Trees By Bike
GMC P0332 Code QA on Low Bank Knock Sensor - Trees By Bike
QA Troubleshooting P0332 Code on 2000 GMC Sierra 48 - Trees By Bike
Chevy Engine Code Lookup - Trees By Bike
How To Decode Chevy Engine Codes - Trees By Bike