Ever noticed your high-powered gadget sputtering when the battery’s supposedly still got juice? That frustrating power fade is the lithium battery voltage drop under load, a fundamental characteristic of these powerhouses. This seemingly simple phenomenon has complex roots, impacting everything from electric vehicles to your pocket-sized devices.
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized portable power, offering high energy density and rechargeability. But the voltage they deliver isn't constant. It fluctuates based on the current draw, or load. Understanding this dynamic is key to optimizing battery life and ensuring consistent performance.
The voltage decrease when a load is applied is a fundamental principle of electrochemistry. It's not a sign of a faulty battery, but rather a consequence of internal resistance. Think of it like a water pipe: the more water you try to force through, the more pressure is lost along the way. Similarly, the higher the current demand from your device, the more voltage the battery loses internally.
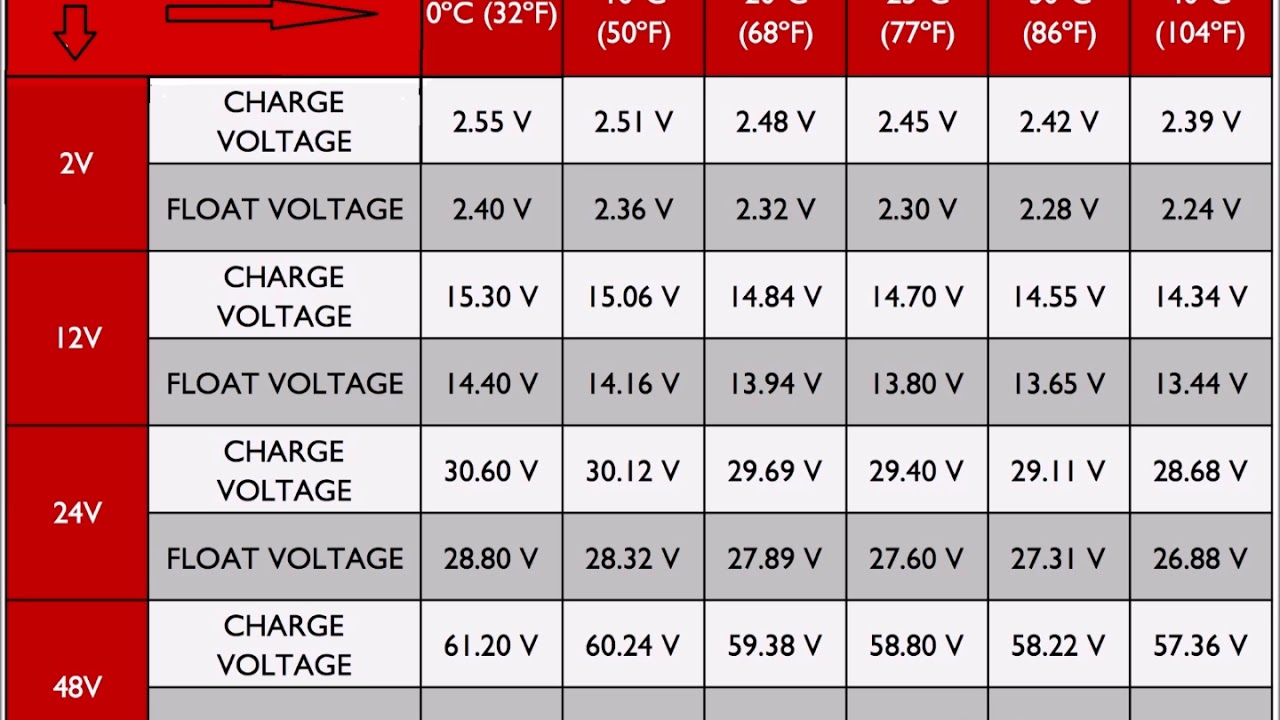
This phenomenon, often referred to as voltage sag, stems from several factors within the battery itself. These include the internal resistance of the battery components, the chemical reactions occurring during discharge, and even the battery's temperature. Understanding these factors is crucial for engineers designing battery-powered systems and for users looking to get the most out of their devices.
Historically, battery voltage drop has been a challenge for engineers. Early battery technologies suffered from even more significant voltage sag, limiting their applications. The development of lithium-ion batteries significantly improved the situation, but the effect remains a consideration in design and usage. The quest for stable voltage output continues to drive research into new battery materials and architectures.
The voltage drop under load is directly related to the internal resistance of the battery. A higher internal resistance leads to a greater voltage drop for a given load. This resistance arises from the various components of the battery, including the electrodes, electrolyte, and current collectors.
Imagine powering a high-drain device like a drone with a lithium-ion battery. As the drone’s motors spin up and demand a large current, the battery voltage dips. This drop can impact the drone’s performance, potentially reducing its flight time or even causing it to malfunction.
One way to mitigate voltage drop is to use batteries with lower internal resistance. Another strategy involves designing circuits that can compensate for the voltage fluctuations. Proper battery management systems can also help by monitoring and regulating the discharge rate.
While managing voltage drop is often seen as a challenge, one could argue a slight voltage dip acts as a built-in safety mechanism, preventing excessive current draw that could damage the battery or the connected device. This perspective highlights the intricate interplay between battery characteristics and device performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Considering Lithium Battery Voltage Drop
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Can indicate battery health | Can lead to performance issues in devices |
| Helps in designing efficient power management systems | Reduces effective battery capacity at high loads |
Best Practices for Managing Lithium Battery Voltage Drop:
1. Select appropriate battery chemistry: Different lithium-ion chemistries exhibit varying internal resistances. Choose a chemistry suited to your application's load demands.
2. Optimize battery temperature: Extreme temperatures can exacerbate voltage drop. Operate batteries within their recommended temperature range.
3. Employ efficient power management circuits: Implement voltage regulators or DC-DC converters to stabilize the output voltage.
4. Monitor battery health: Regularly check the battery's internal resistance to identify potential degradation.
5. Avoid excessive discharge rates: Limit the current draw to minimize voltage sag and prolong battery lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Why does my battery voltage drop under load? (Internal resistance and chemical reactions)
2. Is voltage drop a sign of a bad battery? (Not necessarily, it's a normal phenomenon)
3. How can I minimize voltage drop? (Lower internal resistance batteries, power management circuits)
4. What is the impact of temperature on voltage drop? (Extreme temperatures worsen the effect)
5. How does voltage drop affect battery life? (Excessive drop can shorten lifespan)
6. What is the relationship between internal resistance and voltage drop? (Higher resistance means greater drop)
7. Can voltage drop damage my device? (Yes, if the voltage falls below the device's operating range)
8. How can I measure the internal resistance of my battery? (Specialized battery testers)
Tips and Tricks:
For optimal performance, avoid fully discharging your lithium-ion batteries regularly. Partial discharges are preferable for maximizing lifespan. Also, consider using battery management systems (BMS) to monitor and protect your batteries from over-discharge, over-charge, and excessive temperatures.
In conclusion, lithium battery voltage drop under load is an inherent characteristic that stems from the internal workings of these power sources. While a certain level of voltage drop is normal, understanding its causes and implications is essential for maximizing battery performance and longevity. By considering factors like internal resistance, temperature, and discharge rate, users and engineers can effectively manage voltage drop and ensure reliable operation of their battery-powered devices. The ongoing advancements in battery technology promise to further minimize this effect, leading to even more powerful and efficient energy storage solutions in the future. Investing in quality batteries, implementing proper charging and discharging practices, and understanding the nuances of voltage drop under load will ultimately empower you to harness the full potential of lithium-ion technology. This knowledge is paramount for anyone relying on these batteries, from electric vehicle owners to everyday gadget users. Embrace the power of understanding and unlock the true potential of your lithium-ion batteries.
Calculating Proper Charge Settings for Rolls Flooded Lead - Trees By Bike
Battery Types And Voltage - Trees By Bike
Battery Load Tester Repair at Victoria Neel blog - Trees By Bike
How to read battery discharge curves - Trees By Bike
LiFePO4 Voltage Charts 1 Cell 12V 24V 48V - Trees By Bike
Gel Battery State Of Charge Chart - Trees By Bike
Diagnosing Voltage Drops Electrical Automotive Troubleshooting - Trees By Bike
LiFePo4 Voltage Chart 43 OFF - Trees By Bike
Fully Charged 12 Volt Battery Voltage Chart - Trees By Bike
Are Lithium Iron Phosphate LiFePO4 Batteries Safe A Comprehensive Guide - Trees By Bike
lithium battery voltage drop under load - Trees By Bike
How to read battery discharge curves - Trees By Bike
lithium battery voltage drop under load - Trees By Bike
LiFePo4 Voltage Chart 12V 24V 48V 1 Cell 32V Pro Tips - Trees By Bike
Battery voltage over timetemp formulas anyone - Trees By Bike