Ever glanced at your boat's fuel gauge and felt a pang of uncertainty? Is it truly reflecting the precious liquid gold sloshing around in the tank? Understanding how your boat's fuel gauge works is more than just a matter of convenience; it's about safety, planning, and avoiding the dreaded mid-voyage sputter. This isn't just a needle pointing at a number; it's a window into your vessel's lifeblood.
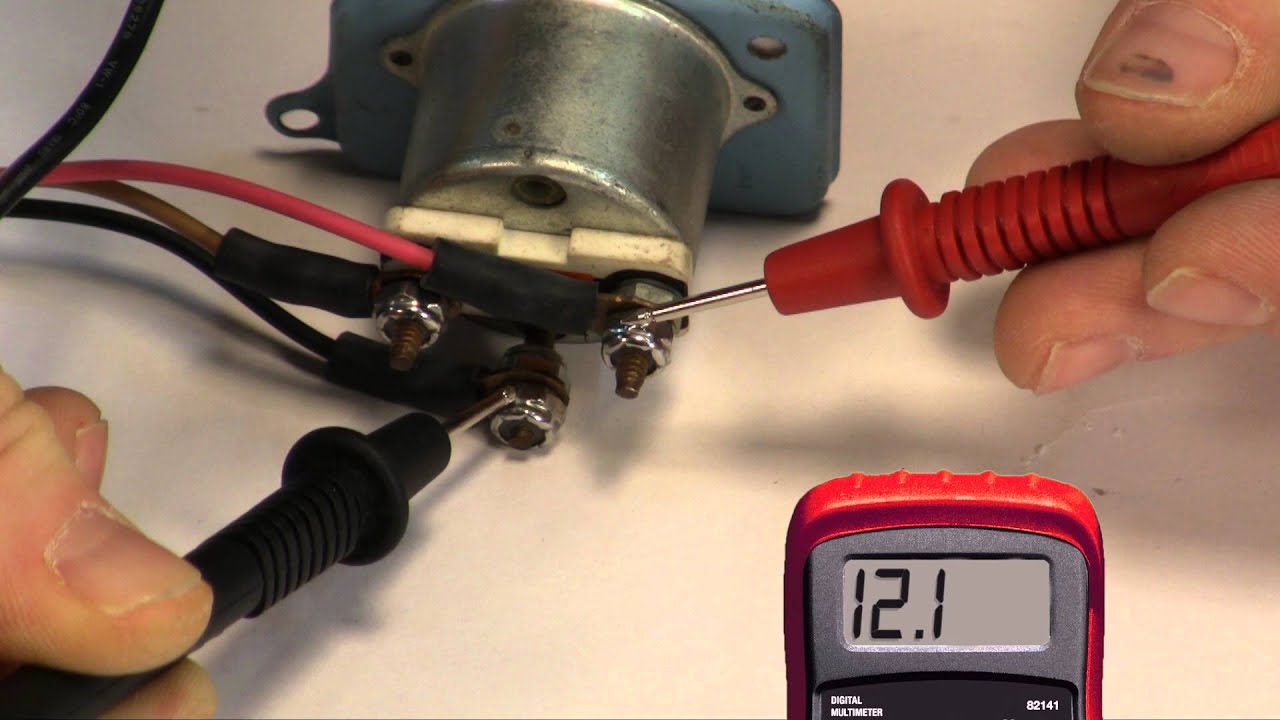
At its core, a boat fuel gauge system is deceptively simple. It's a collaborative effort between a sending unit located in the fuel tank and a gauge on your dashboard. The sending unit, often a float attached to a variable resistor, changes resistance as the fuel level fluctuates. This changing resistance translates into a varying electrical signal, which the gauge interprets and displays as a fuel level reading.
The history of fuel gauges on boats parallels the development of automotive fuel gauges, emerging in the early 20th century as motorized boats gained popularity. Early systems were rudimentary, often relying on mechanical floats connected to levers and dials. The quest for more accurate fuel measurement has driven innovation, leading to the electronic systems prevalent today.
The importance of a functioning fuel gauge is undeniable. Running out of fuel on the water isn't just inconvenient; it's a safety hazard. A reliable gauge allows for accurate trip planning, ensures you have enough fuel to reach your destination, and helps prevent being stranded at sea. Inaccurate fuel level readings can lead to dangerous situations, especially in challenging weather or remote locations.
Several factors can contribute to faulty fuel readings. One common culprit is a malfunctioning sending unit. Corrosion, debris, or a sticking float can throw off the accuracy. Wiring issues, a faulty gauge itself, or even the shape of the fuel tank can all play a role in inaccurate readings.
While the fundamental principles remain the same, different types of boat fuel gauges exist. Analog gauges use a needle and dial, while digital gauges provide a numerical readout. Some newer systems integrate with GPS and chartplotters, providing sophisticated fuel management data.
One major benefit of a reliable fuel gauge is enhanced safety. Knowing your fuel level precisely allows for better trip planning and prevents dangerous situations. Another benefit is improved cost efficiency. Accurate fuel monitoring helps optimize fuel consumption and reduces the risk of running out of fuel and needing costly assistance. Finally, a properly functioning fuel gauge contributes to peace of mind, allowing boaters to relax and enjoy their time on the water without constantly worrying about fuel levels.
Maintaining your boat's fuel gauge is crucial. Regular inspection of the sending unit for corrosion or damage is recommended. Check wiring connections for looseness or corrosion. Periodically test the gauge for accuracy by comparing the reading to a manual dipstick measurement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Fuel Gauge Types
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Analog | Simple, inexpensive | Less precise, susceptible to mechanical failure |
| Digital | Precise, advanced features | More expensive, can be complex to troubleshoot |
Best practices include: regular calibration, checking wiring connections, inspecting the sending unit, and comparing gauge readings with manual dipstick measurements.
Common challenges include faulty sending units, wiring issues, and gauge malfunctions. Solutions involve replacing or repairing the faulty component, cleaning connections, and ensuring proper installation.
Frequently Asked Questions include: How often should I check my fuel gauge? What causes inaccurate readings? How do I troubleshoot a faulty gauge? What are the different types of fuel gauges available? How do I calibrate my fuel gauge? How do I maintain my fuel gauge? What are the signs of a failing fuel gauge? How much does it cost to replace a boat fuel gauge?
Tips and tricks: Use a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel degradation and keep the system clean. Regularly inspect the fuel tank for leaks or corrosion. Consider installing a fuel flow meter for more precise fuel consumption data.
In conclusion, understanding how your boat fuel gauge works is essential for both safety and enjoyment on the water. From the simple float and resistor system to advanced digital displays, the accurate measurement of fuel levels is paramount. Regular maintenance, troubleshooting, and understanding the potential pitfalls will empower you to navigate with confidence, knowing that your next adventure is fueled by knowledge, not just gasoline. By following the best practices outlined and staying informed about the workings of your boat's fuel system, you can ensure smooth sailing and avoid the frustrations and potential dangers of running out of fuel. Taking the time to understand your boat's fuel gauge is an investment in both safety and peace of mind, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: enjoying the open water.
Tach Gauge Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike
Wiring Boat Fuel Gauge - Trees By Bike
Chevy Fuel Gauge Ohms - Trees By Bike
How To Troubleshoot A Boat Fuel Gauge - Trees By Bike
Car Fuel Gauge Circuit Diagram - Trees By Bike
Boat Fuel Gauge Not Working - Trees By Bike
Fuel Gauge Not Working - Trees By Bike
Vn Commodore Fuel Gauge Not Working at Ned Marcello blog - Trees By Bike
how does a boat fuel gauge work - Trees By Bike
Gas Gauge Wiring Diagram For Harley - Trees By Bike
Fuel Tank Gauge Wiring Schematic Diagram - Trees By Bike
how does a boat fuel gauge work - Trees By Bike
Working Principle Of Fuel Gauge - Trees By Bike
Fuel Level Gauges For Tanks - Trees By Bike