Okay, so, like, have you ever looked at your electricity bill and felt utterly bewildered? Those cryptic numbers, the jargon… it’s enough to make you want to ditch the grid and live off the land. But before you start crafting candles by moonlight, let’s talk about something that might actually make your energy bill a little less terrifying: electricity price caps.
Electricity price cap unit rates. Even the name sounds intimidating, right? But essentially, these are limits set on how much energy suppliers can charge you per unit of electricity (usually measured in kilowatt-hours or kWh). Think of it like a financial guardrail, preventing your bill from spiraling into the stratosphere.
These price ceilings aren't just arbitrary figures plucked from thin air. They’re often implemented by regulatory bodies to protect consumers from exorbitant energy costs, especially during times of market volatility. Understanding how these caps work can empower you to make informed decisions about your energy consumption and potentially even save some money.
The history of electricity price regulation is long and complex, varying significantly across different countries and regions. Early forms of regulation often focused on ensuring reliable service and preventing monopolies. However, the focus shifted towards consumer protection and affordability with the increasing liberalization of energy markets. Price caps emerged as a key tool in this effort, aiming to strike a balance between affordable energy for consumers and fair returns for energy suppliers.
The importance of electricity price cap unit rates is particularly evident during periods of energy price spikes, as seen recently in many parts of the world. Without these caps, consumers could be exposed to dramatic price increases, leading to financial hardship. However, setting the right level for a price cap is a delicate balancing act. Caps set too low could discourage investment in the energy sector, leading to supply shortages in the long run. Conversely, caps set too high fail to provide adequate consumer protection.
A key issue surrounding price caps is their complexity. Different regions have different methodologies for calculating and implementing these caps, often incorporating various factors such as network costs, wholesale energy prices, and supplier operating costs. This complexity can make it challenging for consumers to understand how the cap affects their bill and whether they are getting a fair deal.
One significant benefit of electricity price caps is increased price transparency. By establishing a ceiling, regulators promote clearer pricing structures, allowing consumers to compare offers from different energy suppliers more easily. This fosters competition and empowers consumers to choose the most cost-effective option.
Another advantage is enhanced consumer protection, especially for vulnerable households. Price caps provide a safety net against volatile market fluctuations, preventing unexpected surges in energy bills and ensuring access to affordable essential services.
Finally, price caps can promote energy efficiency. By setting limits on unit rates, regulators incentivize consumers to reduce their energy consumption to manage their bills. This can contribute to overall energy conservation and a smaller environmental footprint.
One simple example: imagine your price cap is set at $0.15 per kWh. If you use 1000 kWh in a month, your maximum energy charge would be $150, excluding other charges like standing charges. If the market price were to rise above $0.15, the cap would protect you from paying the higher rate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electricity Price Caps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Consumer protection from high prices | Potential disincentive for supplier investment |
| Increased price transparency | Possible supply shortages in the long term |
| Promotion of energy efficiency | Complexity of implementation and oversight |
For tips and tricks on navigating the world of electricity price caps, start by thoroughly researching your local regulations and the specific details of your energy plan. Compare offers from different suppliers and consider factors such as contract length and renewable energy options. Utilize online comparison tools and resources provided by consumer advocacy groups to ensure you're getting the best deal possible.
In conclusion, understanding electricity price cap unit rates is crucial for navigating the often-confusing landscape of energy bills. While the specifics can be complex, the underlying principle is simple: to protect consumers from unfair pricing and promote a more stable and transparent energy market. By taking the time to learn about these rate limits, comparing offers, and staying informed about changes in regulations, you can take control of your energy costs and make informed decisions that benefit both your wallet and the planet. So, go forth, energy empowered, and decode those bills!
Electricity Prices Uk at Peter Berke blog - Trees By Bike
Electricity Prices Uk at Peter Berke blog - Trees By Bike
Energy prices from January - Trees By Bike
electricity price cap unit rates - Trees By Bike
How Much Will Energy Prices Rise In 2024 - Trees By Bike
The electricity price rise in January 2023 will be around 20 and the - Trees By Bike
Energy Price Cap Forecast October 2024 Forecast - Trees By Bike
electricity price cap unit rates - Trees By Bike
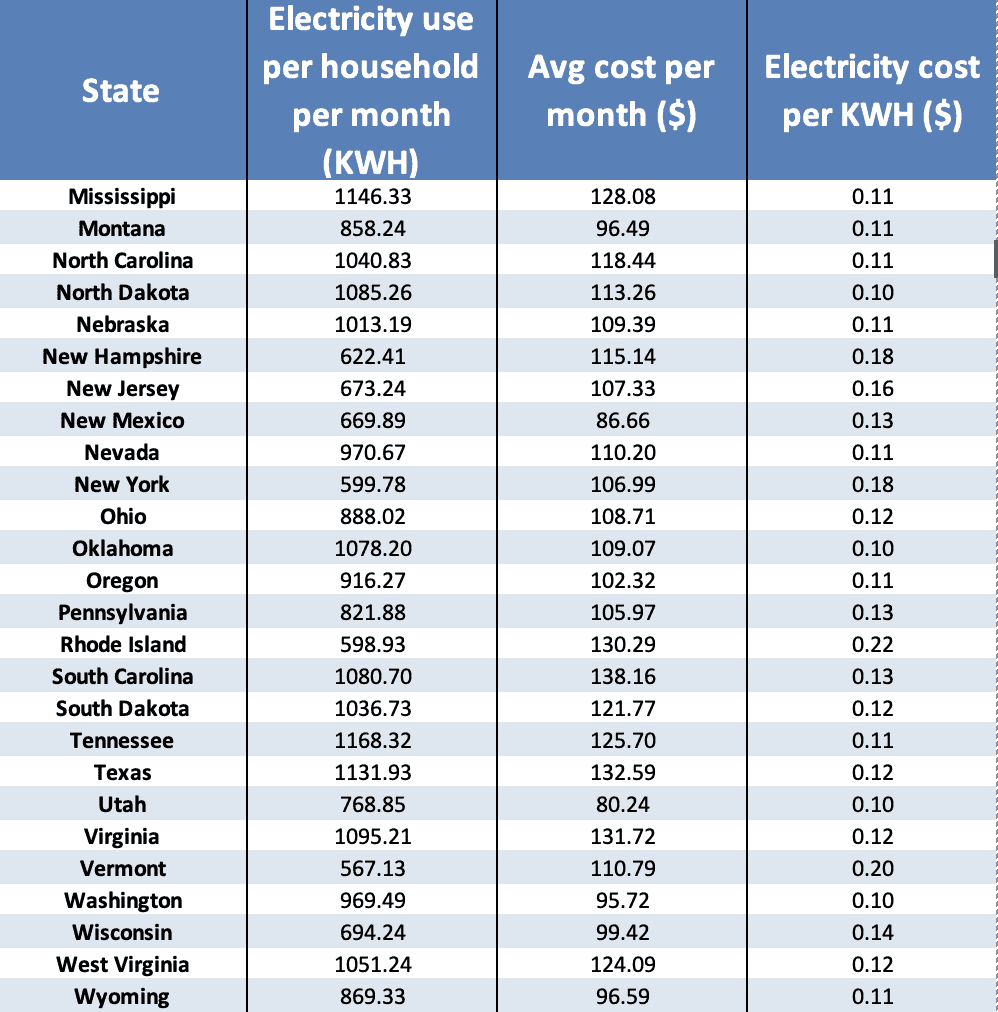
Average Household Electricity Consumption - Trees By Bike
Electricity Price Uae at Lai Morin blog - Trees By Bike
electricity price cap unit rates - Trees By Bike
50 best ideas for coloring - Trees By Bike
Savings on energy bills this winter as price cap falls - Trees By Bike
Energy Costs In Europe 2024 - Trees By Bike
Electricity Bill Unit Price 2024 - Trees By Bike