Imagine a world without water, air, or even you. Impossible, right? Now, picture these essential elements broken down into their tiniest, most fundamental components. These minuscule building blocks are what we call molecules, the unsung heroes of our physical world.
But what exactly does a molecule mean? Simply put, a molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. These bonds, like tiny, powerful magnets, arise from the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms. This seemingly simple concept of atoms joining forces unlocks a universe of complexity and diversity, giving rise to everything we see, touch, and experience.
From the air we breathe, composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen molecules, to the intricate proteins that make up our bodies, the presence of molecules is ubiquitous and essential. Understanding what a molecule means is key to unlocking the secrets of chemistry, biology, and the very nature of our existence.
The concept of the molecule, while seemingly fundamental today, was not always so clearly defined. Ancient Greek philosophers like Democritus pondered the idea of indivisible particles, but it wasn't until the 19th century that the true nature of molecules began to emerge. Scientists like John Dalton, Amedeo Avogadro, and Dmitri Mendeleev played pivotal roles in developing atomic theory and understanding how these tiny particles combine to form the matter we see around us.
The study of molecules has revolutionized our understanding of the world. It has given us the tools to develop life-saving drugs, create new materials with astonishing properties, and unlock the secrets of life itself. Yet, despite the incredible advancements in our understanding, molecules continue to surprise us, pushing the boundaries of scientific exploration and reminding us of the infinite complexity hidden within the seemingly mundane.
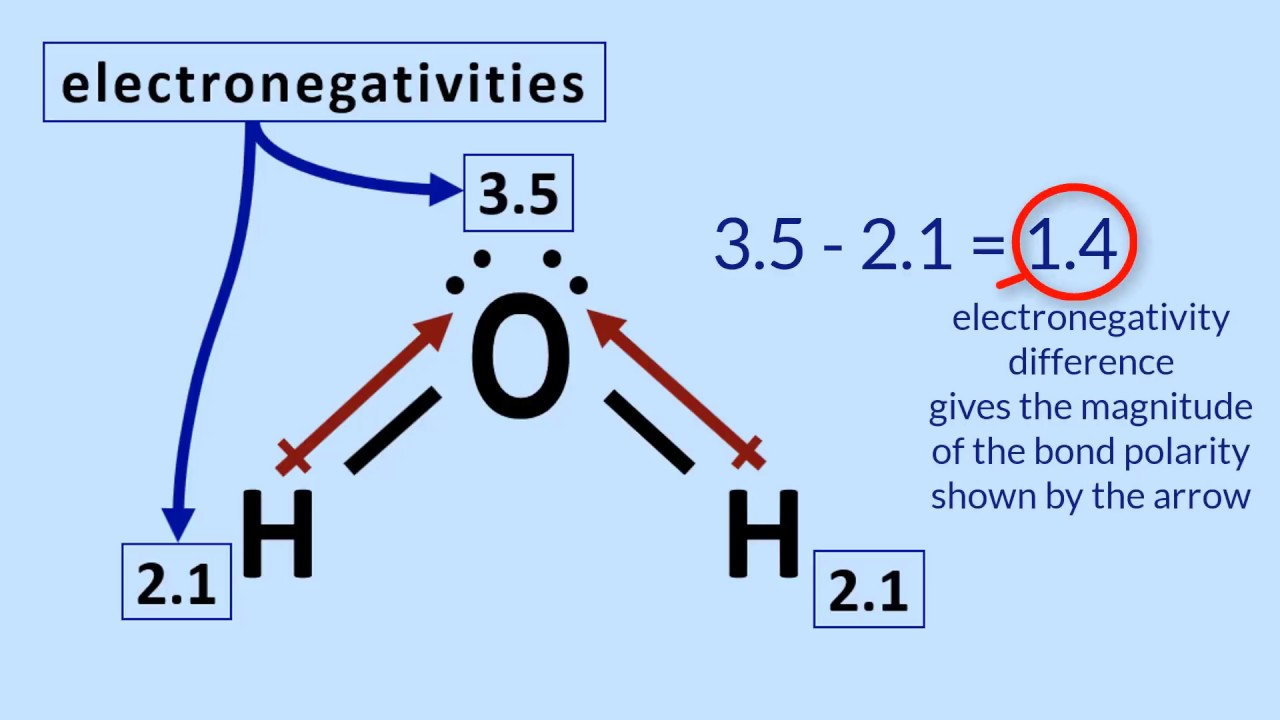
Let's delve further into the realm of molecules. A simple example is water, represented by the chemical formula H2O. This tells us that a single water molecule comprises two hydrogen atoms (H) bonded to one oxygen atom (O). Another example is carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas, consisting of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. These simple examples illustrate how the type and arrangement of atoms within a molecule dictate its properties and behavior.
The importance of understanding what a molecule means cannot be overstated. This fundamental concept underpins numerous fields, including:
Medicine: Drug development relies heavily on understanding how molecules interact with the body. By designing molecules that bind to specific targets, scientists can create medications that treat diseases and improve human health.
Materials Science: The properties of materials, from the strength of steel to the flexibility of plastic, are determined by the types of molecules they contain and how these molecules are arranged. By manipulating molecular structures, scientists can create innovative materials with tailored properties.
Environmental Science: Understanding the behavior of molecules in the environment is crucial for addressing issues like pollution and climate change. By studying how pollutants interact with atmospheric molecules, we can develop strategies to mitigate their impact on our planet.
In conclusion, while the concept of a molecule might seem abstract, its implications are far-reaching and profoundly impact our daily lives. From the air we breathe to the medicines we rely on, molecules are the fundamental building blocks of our universe. Grasping the meaning of a molecule opens up a world of understanding, allowing us to appreciate the complexity and elegance of the natural world and empowering us to develop innovative solutions to global challenges.
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
Ammonia (NH3), Molecular Model Vector Illustration - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
Polarity Of Molecules Practice - Trees By Bike
How To Determine Nonpolar Covalent Bond - Trees By Bike
Isomers of Organic Compounds - Trees By Bike
what does a molecule mean - Trees By Bike
What are Atoms & Molecules? - Trees By Bike