Imagine biting into a sun-ripened tomato plucked straight from your garden, not in the peak of summer, but in the heart of winter. This isn’t a fantasy; it’s the reality of year-round vegetable gardening in Florida. The Sunshine State’s unique subtropical climate presents a compelling opportunity for continuous harvests, transforming your backyard into a veritable Eden of fresh produce. But how do you navigate the nuances of Florida’s distinct growing seasons? This is your guide to disrupting the traditional gardening calendar and embracing the bounty of Florida’s year-round potential.
Florida's long growing season isn't just a recent trend; it's woven into the state's agricultural history. From indigenous communities cultivating native crops to the arrival of Spanish settlers introducing new varieties, Florida has a rich heritage of cultivating the land. This legacy continues today, with home gardeners across the state tapping into the potential for year-round harvests. This sustainable practice not only reduces reliance on commercially grown produce but also connects individuals with the land in a meaningful way.
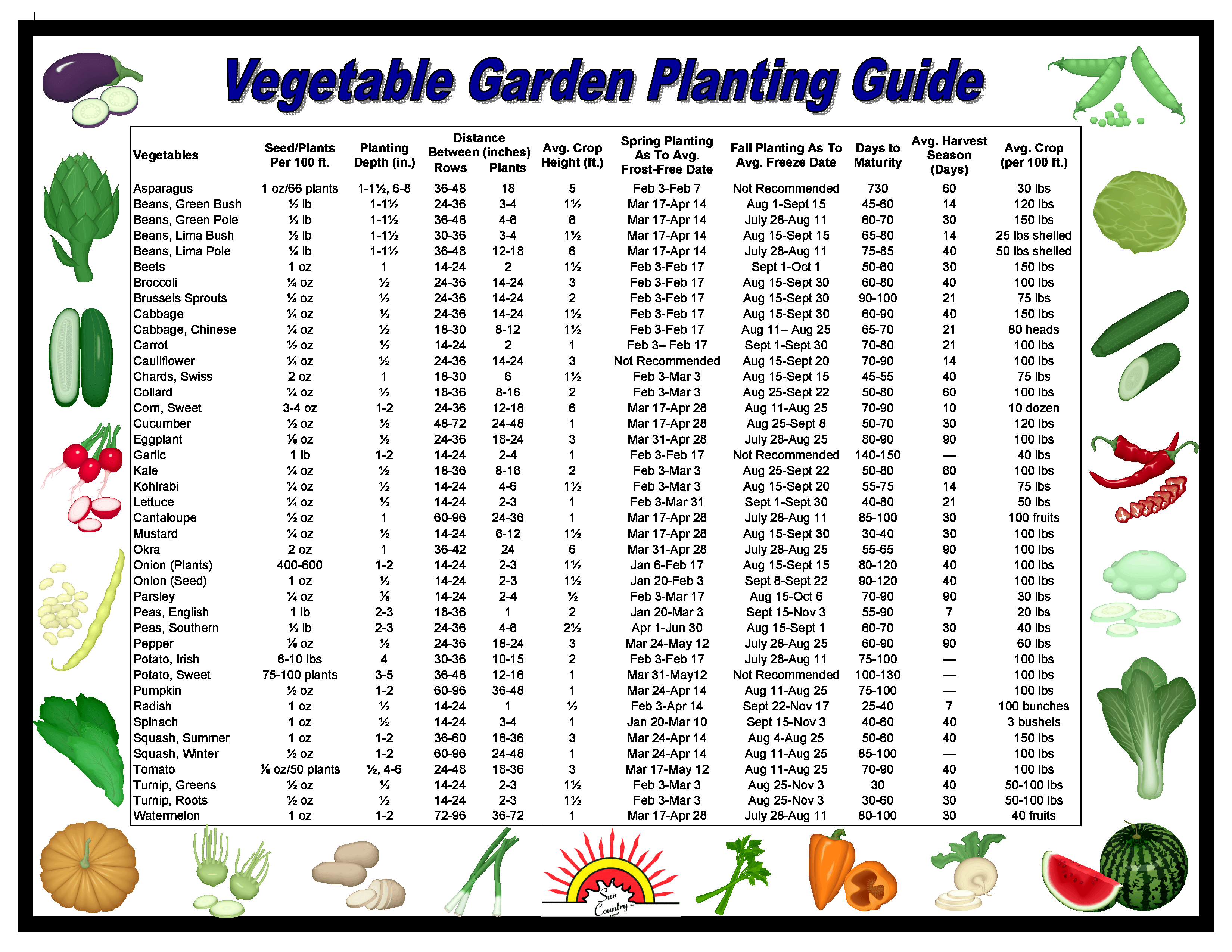
The key to Florida vegetable gardening lies in understanding the two distinct growing seasons: the warm season (spring/summer) and the cool season (fall/winter). Warm-season crops thrive in the heat and humidity, while cool-season crops prefer milder temperatures. Mastering this seasonal dance is essential for maximizing your yields. One of the main challenges, however, is managing pests and diseases, which can proliferate in Florida’s warm, humid environment. Another obstacle is navigating the occasional extreme weather events, like hurricanes and freezes, which can disrupt the growing cycle.
Successfully cultivating vegetables year-round in Florida involves selecting the right crops for each season. Warm-season vegetables include staples like tomatoes, peppers, beans, and squash. Cool-season vegetables encompass leafy greens like lettuce, spinach, kale, and root crops like carrots and radishes. Choosing varieties that are well-suited to Florida's climate is crucial for a bountiful harvest. For example, heat-tolerant tomato varieties are a must for summer gardening, while cold-hardy greens are essential for winter success.
One of the major benefits of year-round gardening is the continuous supply of fresh, homegrown produce. This translates to healthier meals, reduced grocery bills, and a deeper connection with the food you consume. Another advantage is the ability to experiment with a wider range of vegetables. Florida's climate allows gardeners to cultivate varieties that wouldn't thrive in other regions, opening up a world of culinary possibilities. Finally, gardening itself offers therapeutic benefits, providing a connection to nature and a sense of accomplishment.
To achieve year-round success, consider these best practices: choose the right location with adequate sunlight, amend your soil with compost and other organic matter, implement proper watering techniques, utilize pest and disease control methods, and rotate crops to maintain soil health.
Real examples of successful year-round gardens in Florida include community gardens utilizing raised beds, vertical gardening systems maximizing space in urban environments, and hydroponic setups enabling year-round growth regardless of soil conditions.
Challenges include pest infestations, which can be addressed with integrated pest management techniques. Intense summer heat requires careful watering and shading strategies. Heavy rainfall can lead to fungal diseases, necessitating preventative measures. Occasional freezes necessitate protecting vulnerable plants. Finally, the abundance of certain crops during peak seasons requires preservation methods like canning or freezing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Year-Round Vegetable Gardening in Florida
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Fresh produce year-round | Pest and disease pressure |
| Reduced grocery bills | Potential for crop damage from extreme weather |
| Wider variety of crops | Requires consistent effort and maintenance |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What vegetables can I grow in Florida during the winter? Leafy greens, root crops, and some brassicas.
2. What are the best tomatoes for Florida summers? Heat-tolerant varieties like Solar Fire and Florida 91.
3. How do I manage pests in my Florida garden? Utilize integrated pest management strategies.
4. When should I start seeds for my fall garden? Late summer.
5. How can I protect my plants from frost? Use row covers or bring potted plants indoors.
6. What are the best fertilizers for Florida soil? Balanced fertilizers with micronutrients.
7. How often should I water my vegetables in Florida? Depends on the season and specific plant needs.
8. Where can I learn more about Florida gardening? UF/IFAS Extension offices and local gardening groups.
Tips and tricks: Start seeds indoors during colder months. Utilize trellises for vining crops. Mulch to conserve moisture and suppress weeds. Practice crop rotation to maintain soil health.
Embracing year-round vegetable gardening in Florida is more than just a hobby; it's a lifestyle that connects you to the land, fosters sustainability, and provides a continuous source of fresh, nutritious food. By understanding the nuances of Florida’s climate and employing the right techniques, you can transform your backyard into a thriving ecosystem, producing a bounty of delicious vegetables year after year. From reducing your carbon footprint to savoring the flavor of a homegrown tomato in December, the benefits of cultivating your own Florida garden are undeniable. Take the leap and unlock the potential of year-round gardening – you'll be amazed by what you can achieve.
Seasonal Vegetables Southern California at David Tineo blog - Trees By Bike
What Vegetables To Grow In Zone 8 - Trees By Bike
Shrubs Colorful at Lillian Cramer blog - Trees By Bike
Florida Vegetable Growing Calendar - Trees By Bike
Growing Tomatoes Year Round In Greenhouse at Anne Mcdonald blog - Trees By Bike
Easy Vegetables to Grow - Trees By Bike
What foods are grown in virginia 11 Famous Foods From Virginia Dishes - Trees By Bike
What Vegetables Grow Fast From Seed at Dominic Thornburg blog - Trees By Bike
17 Best Flowers That Grow In Florida Year - Trees By Bike
Heavy Rain Forecast for Florida in Days Ahead - Trees By Bike
growing vegetables in florida year round - Trees By Bike
Florida Growing Seasons For Vegetables Chart - Trees By Bike
growing vegetables in florida year round - Trees By Bike
Grow Fruits And Vegetables Charts - Trees By Bike
A3 novice allotment planner gardenersbeginners vegetable growing - Trees By Bike