Ever wondered how electrical engineers tame the wild, oscillating currents of alternating current (AC) circuits? They wield a powerful tool: the phasor. Phasors are more than just a cool name; they are the key to simplifying complex AC circuit analysis. This article explores the fascinating world of phasors and their graphical counterpart, phasor diagrams, revealing how they transform complex calculations into manageable visualizations.
Imagine trying to analyze a circuit with constantly changing voltages and currents. The math can quickly become a nightmare. Phasors offer an elegant solution by representing these sinusoidal quantities as static vectors, allowing engineers to apply algebraic techniques instead of grappling with differential equations. This simplification is a game-changer, enabling efficient analysis of intricate AC circuits.
Phasor diagrams provide a visual representation of these phasor quantities. They illustrate the relationships between voltage and current in a circuit, making it easier to grasp the overall circuit behavior. By depicting the magnitude and phase angle of each phasor, these diagrams offer a clear snapshot of the circuit's operation at a specific frequency.
The concept of the phasor arose from the need to simplify AC circuit calculations. Early electrical engineers recognized the challenges posed by sinusoidal quantities and sought a more streamlined approach. The development of phasor analysis marked a significant advancement in the field, paving the way for the design and analysis of more complex electrical systems.
The fundamental principle behind phasor analysis is the representation of sinusoidal functions as rotating vectors. The magnitude of the vector corresponds to the amplitude of the sinusoid, while its angle represents the phase shift. This transformation converts time-varying quantities into static vectors, making them amenable to simpler mathematical manipulation.
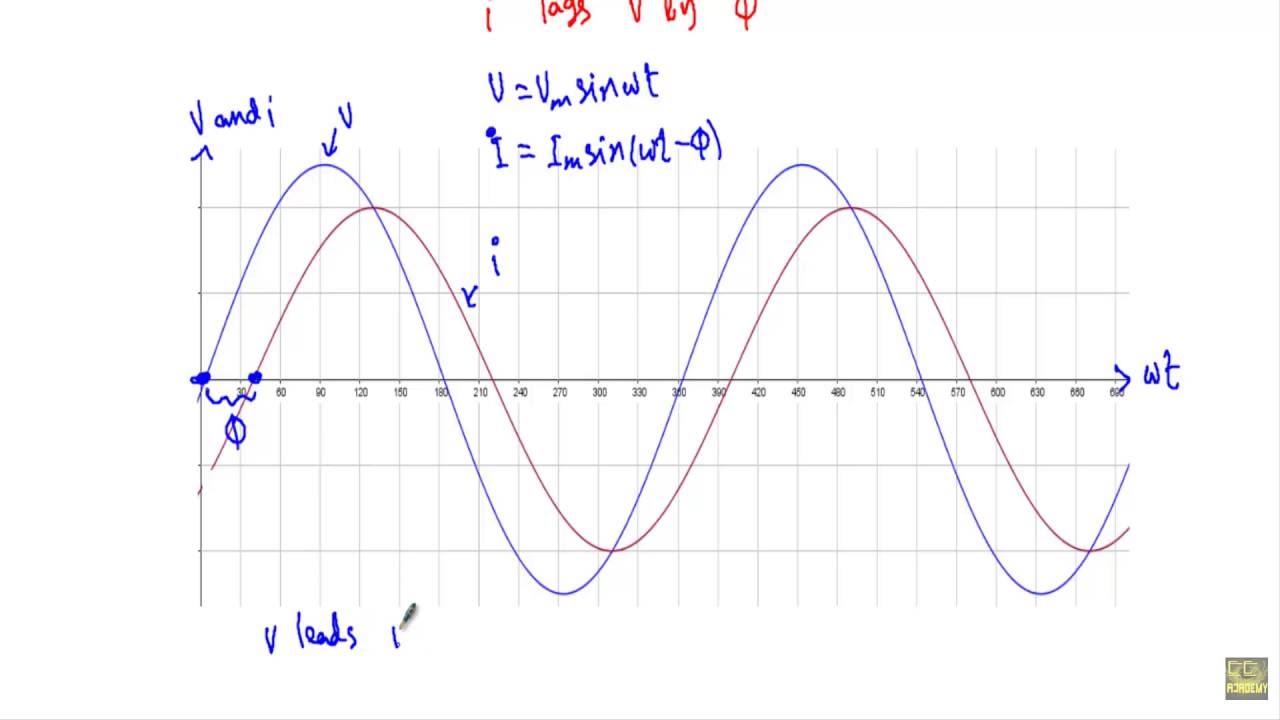
A phasor diagram is a graphical representation of phasors within a specific circuit. It visually displays the relationships between voltage and current phasors, allowing engineers to quickly assess circuit behavior. The relative positions and lengths of the phasors indicate their phase differences and magnitudes.
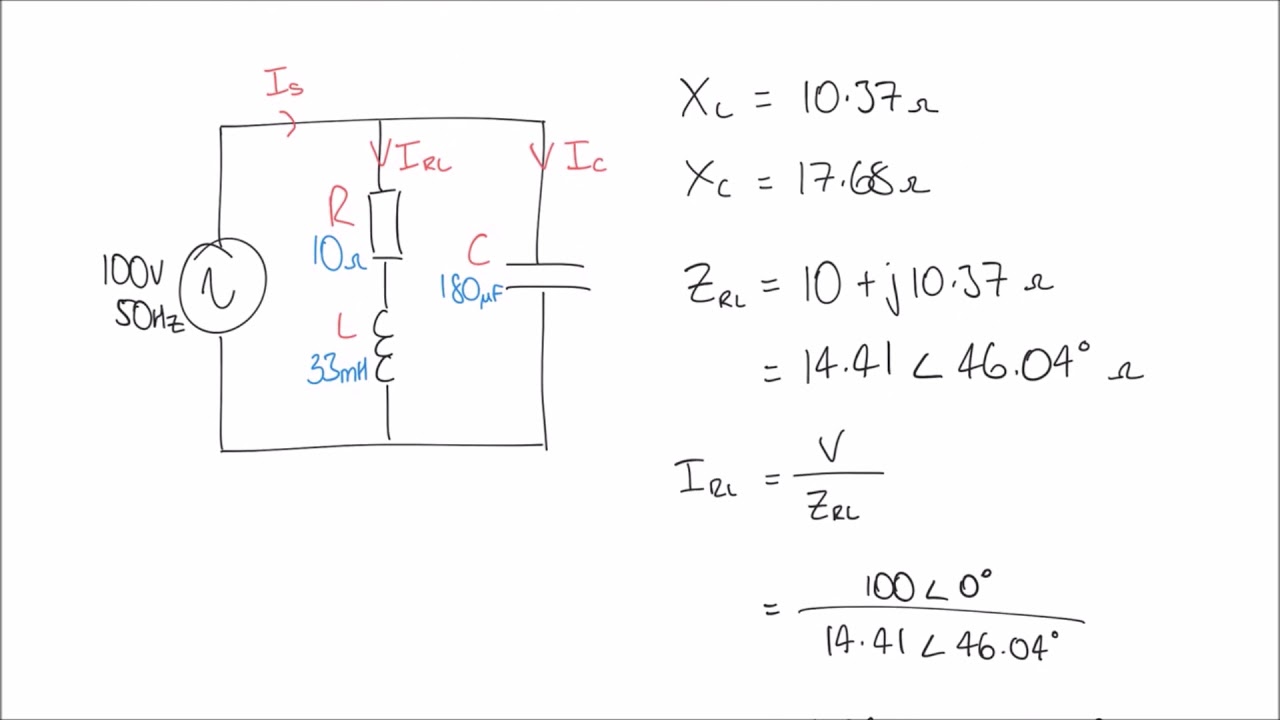
Benefits of using phasors and phasor diagrams include simplified calculations, improved visualization of circuit behavior, and easier understanding of complex AC circuits. For example, calculating the total impedance of a circuit with multiple components becomes much simpler using phasor addition than solving differential equations.
Implementing phasor analysis involves converting sinusoidal voltages and currents into their phasor representations, performing calculations using complex numbers, and then converting the results back to the time domain if necessary. Understanding the relationship between the frequency of the sinusoids and the angular velocity of the phasors is crucial.
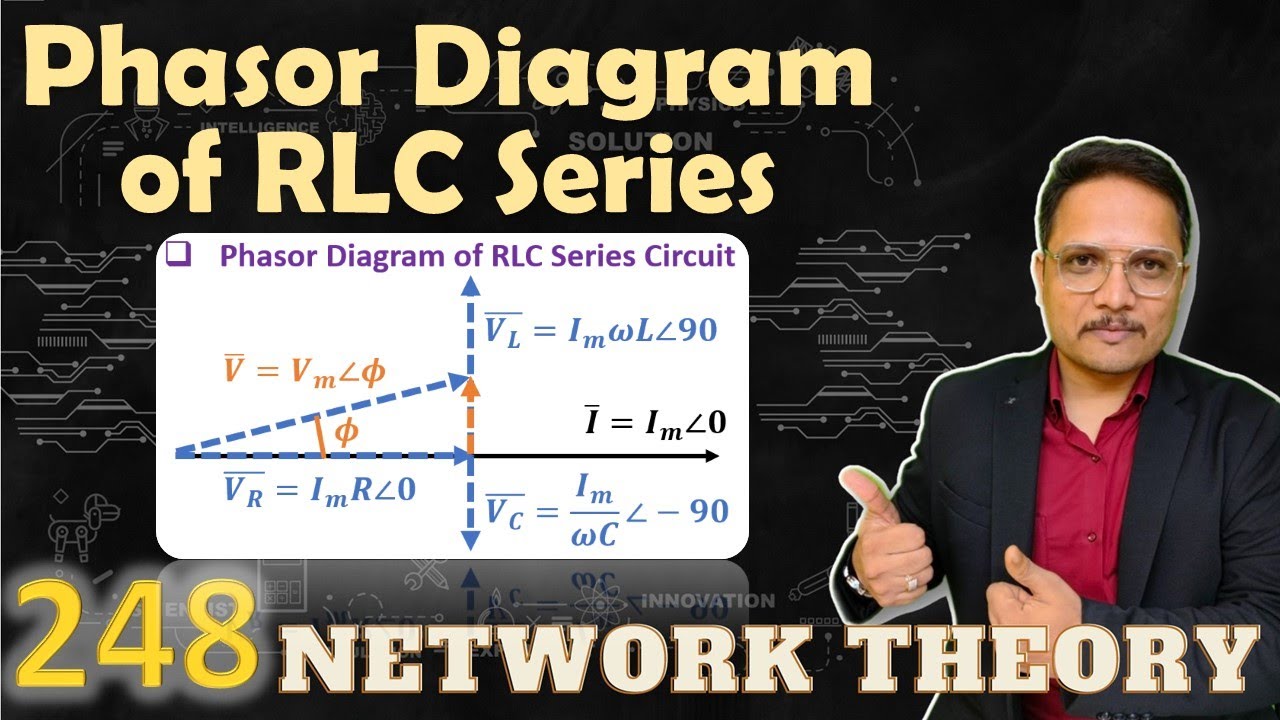
A simple example: Consider a series circuit with a resistor and an inductor. Using phasor analysis, the voltage across each component can be represented as a phasor. The voltage across the resistor is in phase with the current, while the voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90 degrees. The phasor diagram clearly illustrates this phase relationship.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplified AC circuit analysis | Limited to steady-state sinusoidal analysis |
| Visual representation of circuit behavior | Doesn't directly represent transient behavior |
| Facilitates understanding of phase relationships | Can be complex for highly intricate circuits |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? - A representation of a sinusoidal quantity as a rotating vector.
2. What is a phasor diagram? - A graphical representation of phasors in a circuit.
3. Why are phasors used? - To simplify AC circuit analysis.
4. What is the significance of the phasor angle? - It represents the phase shift of the sinusoid.
5. How are phasors related to complex numbers? - Phasors are often represented using complex numbers.
6. What are the limitations of phasor analysis? - It is primarily applicable to steady-state sinusoidal analysis.
7. How are phasor diagrams helpful? - They provide a visual understanding of circuit behavior.
8. Can phasor diagrams be used for non-sinusoidal waveforms? - No, they are specifically for sinusoidal waveforms.
In conclusion, phasors and phasor diagrams are invaluable tools in electrical engineering. They simplify the analysis of AC circuits, providing a visual and intuitive way to understand complex relationships between voltage, current, and impedance. While they primarily apply to steady-state sinusoidal analysis, their importance in electrical power systems, electronics, and telecommunications cannot be overstated. By mastering phasor representation, engineers can unlock a deeper understanding of AC circuit behavior and design more efficient and robust electrical systems. Explore the world of phasors and elevate your understanding of electrical engineering to new heights. Take the time to learn and apply these concepts, and you'll find a powerful new tool in your engineering toolkit.
phasor and phasor diagram - Trees By Bike
Locus Diagram Of Series Rlc Circuit - Trees By Bike
What is a phasor diagram - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Of Rlc Circuit - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit Series - Trees By Bike
What is RLC Series Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram Derivation - Trees By Bike
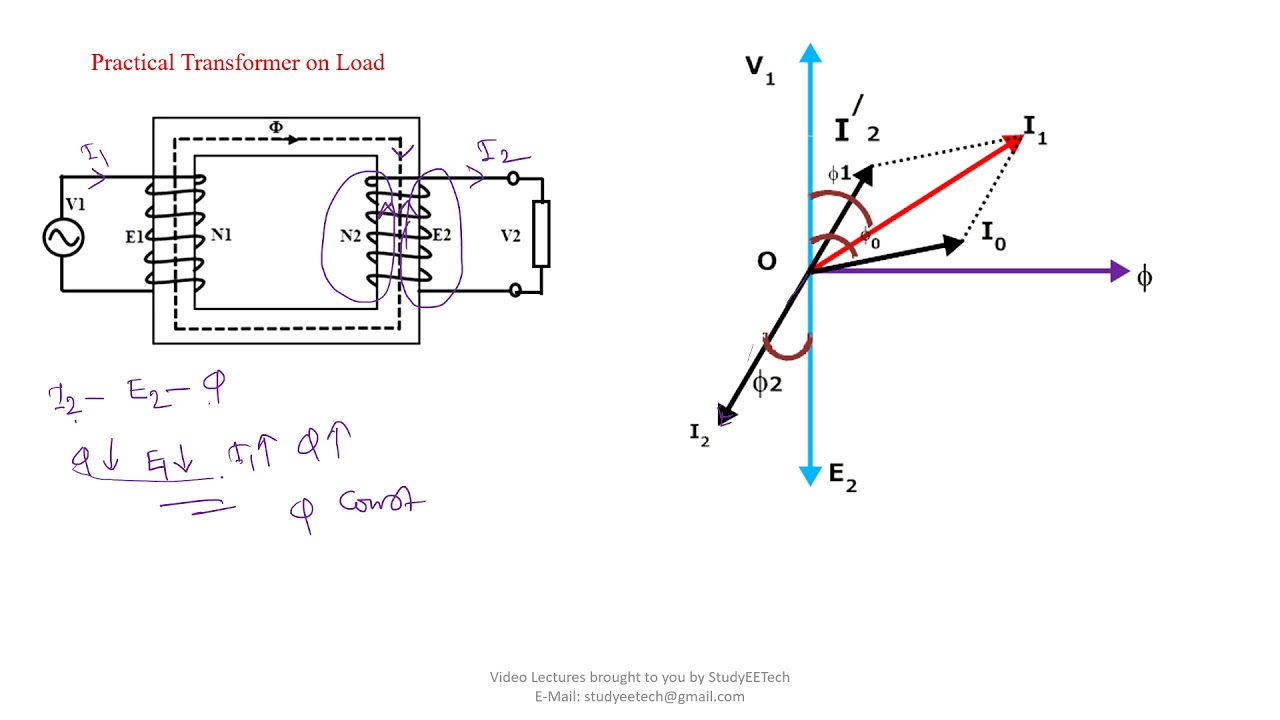
Phasor Diagram Of Transformer Equivalent Circuit - Trees By Bike
phasor and phasor diagram - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Of Capacitor In Ac Circuit - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram For Ac Circuit - Trees By Bike
Three Phase Delta Connection Three Phase PowerVoltageCurrent - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Of Transformer On No Load - Trees By Bike
RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Trees By Bike
phasor and phasor diagram - Trees By Bike
Rl Circuit Phasor Diagram - Trees By Bike