There's a certain quiet hum that a well-functioning home possesses, an almost invisible current of energy that powers our everyday lives. But when that hum falters, when a flicker becomes a blackout, it's often the unassuming circuit breaker that takes center stage. Knowing how to address a faulty breaker, understanding the subtle art of its replacement, becomes not just a practical skill but a necessity.
A circuit breaker, in its essence, is a safety device designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in the event of an overload or short circuit. Imagine it as a vigilant guardian, constantly monitoring the electrical currents within your walls, ready to intervene when things go amiss. Replacing a circuit breaker is a task that requires careful attention to detail and a respect for the power it controls. While it might seem daunting, with the right guidance and precautions, it's a manageable process.
The history of circuit breakers dates back to the late 19th century, evolving from simple fuses to the sophisticated devices we have today. Early forms were crude but effective, breaking the circuit with a visible spark and requiring manual reset. The need for a more reliable and reusable solution led to the development of modern circuit breakers, which automatically trip and can be easily reset.
Understanding the importance of correctly replacing a circuit breaker is paramount for electrical safety. A faulty breaker can lead to overheating, fires, and even electrocution. Proper replacement ensures that the electrical system in your home or building continues to operate safely and efficiently, protecting both your property and your well-being. Common issues that necessitate circuit breaker replacement include frequent tripping, a burning smell, physical damage, or an outdated breaker that no longer meets current safety standards.
Before embarking on a replacement, identifying the correct amperage for the new breaker is crucial. The amperage, measured in amps, indicates the maximum current the breaker can handle. Using a breaker with the wrong amperage can be dangerous, either providing insufficient protection or tripping unnecessarily. Consult the markings on the old breaker or a qualified electrician to determine the correct amperage for your specific circuit.
One benefit of mastering circuit breaker replacement is the cost savings. While calling an electrician is always a viable option, especially for complex situations, replacing a simple breaker is a task many homeowners can tackle themselves, saving on service fees.
Another advantage is the increased sense of self-reliance and empowerment that comes with understanding the inner workings of your home's electrical system. This knowledge translates into a greater ability to troubleshoot minor electrical problems and maintain a safe environment.
Lastly, being able to quickly replace a faulty breaker minimizes downtime. Instead of waiting for an electrician to become available, you can restore power promptly, minimizing inconvenience and potential damage to appliances or electronic devices.
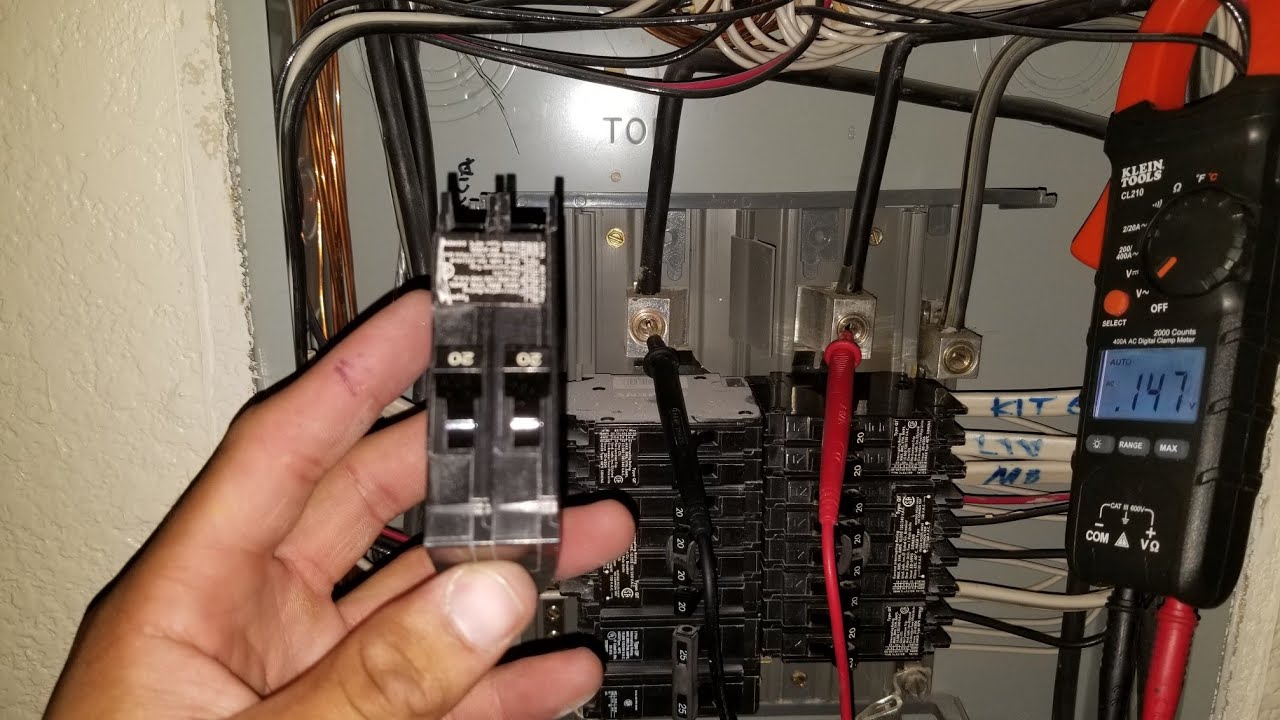
Here's a simplified step-by-step guide for replacing a single-pole circuit breaker:
1. Turn off the main power to the panel.
2. Remove the panel cover, exercising extreme caution.
3. Locate the faulty breaker.
4. Loosen the terminal screw and disconnect the wire from the old breaker.
5. Remove the old breaker.
6. Install the new breaker, ensuring it's securely in place.
7. Connect the wire to the new breaker, tightening the terminal screw.
8. Replace the panel cover.
9. Turn the main power back on.
10. Test the new breaker.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DIY Circuit Breaker Replacement
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost savings | Risk of electrical shock or injury |
| Increased self-reliance | Potential for incorrect installation |
| Minimized downtime | May void warranties if improperly done |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Do I need to turn off the main power? Yes, always.
2. Can I replace a breaker with a higher amperage? No, unless the wiring supports it and after consulting an electrician.
3. What if the new breaker trips immediately? This could indicate a wiring problem.
4. What tools do I need? Screwdriver, voltage tester.
5. Should I call an electrician? If you're unsure, yes.
6. How often should breakers be replaced? Typically when they fail or become outdated.
7. What are signs of a bad breaker? Frequent tripping, burning smell, physical damage.
8. Can I replace a double-pole breaker myself? This is more complex and it's generally recommended to call an electrician.
The ability to confidently and safely replace a circuit breaker is a skill that empowers homeowners and ensures the continued safety and functionality of their electrical systems. From the quiet hum of a properly functioning circuit to the peace of mind that comes with knowing how to handle a potential electrical issue, understanding the nuances of circuit breaker replacement is a valuable asset. This knowledge provides not only practical benefits but also a deeper connection to the intricate network that powers our modern lives.
How To Replace Main Circuit Breaker - Trees By Bike
Circuit Breaker Will Not Come Back On at Michelle Hawks blog - Trees By Bike
How To Replace Main Circuit Breaker - Trees By Bike
How To Repair Electrical Outlet House Flipper - Trees By Bike
How To Add A Circuit Breaker An Existing Panel - Trees By Bike
Ground Fault Outlet Wiring - Trees By Bike
circuit breaker how to replace - Trees By Bike
Replace 15 Amp Breaker With 20 Amp - Trees By Bike
Can I Replace A Fuse With A Circuit Breaker - Trees By Bike
2014 Polaris Sportsman 570 EFI 10A fan circuit breaker location - Trees By Bike
How To Replace Electrical Breaker In Main Box - Trees By Bike
How To Replace A Circuit Breaker In A House - Trees By Bike
circuit breaker how to replace - Trees By Bike
How To Replace Main Circuit Breaker - Trees By Bike
Replace Fuse In Circuit Breaker - Trees By Bike


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/safely-install-a-circuit-breaker-1152745-08-6f6a59afc5a24dd189ef645617d1ee54.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/safely-install-a-circuit-breaker-1152745-03-d92d49657a664c6ba820c461a0643f24.jpg)





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/safely-install-a-circuit-breaker-1152745-05-c8ed0d03a8814435870663dd1b407763.jpg)


