In the realm of construction and manufacturing, precision is paramount. A seemingly minor discrepancy in measurement can have cascading effects, impacting everything from structural integrity to the aesthetic harmony of a finished product. This is where the understated elegance of standardized key steel sizes in the metric system comes into play. Much like a perfectly tailored suit, the right dimensions are crucial for a seamless fit and optimal performance.
Consider the framework of a modern building, the skeleton upon which its skin of glass and concrete rests. Each steel beam, each column, each meticulously placed element adheres to specific metric steel size standards, ensuring the building's stability and resilience. These standardized dimensions, a language understood universally across industries, are the invisible threads that hold our built environment together.
The metric system, with its logical decimal-based structure, provides a common ground for designers, engineers, and fabricators worldwide. It streamlines communication, eliminates ambiguity, and facilitates the smooth exchange of information, materials, and expertise across borders. This global standardization is especially critical in the steel industry, where projects often involve international collaboration.
But how did we arrive at these standard metric steel sizes? The history of standardized dimensions is intertwined with the evolution of the metric system itself, a story of scientific advancement and international cooperation. The adoption of the metric system in the late 18th century marked a pivotal shift towards uniformity in measurement, paving the way for the development of standardized steel sizes that are used today.
Understanding these standardized dimensions is not just about knowing the numbers; it's about appreciating the underlying principles of efficiency, precision, and interoperability. It's about recognizing the subtle but significant role that these standardized key steel sizes play in shaping the world around us, from the soaring skyscrapers that define our cityscapes to the intricate mechanisms that power our industries.
The importance of utilizing standardized metric steel sizes is multifaceted. It promotes cost-effectiveness by minimizing material waste and simplifying fabrication processes. It enhances safety by ensuring structural integrity and predictable performance. And it fosters global collaboration by establishing a common language for design and construction.
One key issue related to metric steel sizes is ensuring accurate conversion from other measurement systems. Errors in conversion can lead to significant discrepancies, compromising the integrity of a project. Therefore, meticulous attention to detail and the use of reliable conversion tools are crucial.
A simple example of a standardized metric steel size is a 100 mm x 100 mm x 10 mm angle. This designation indicates the dimensions of the angle's legs and its thickness. This clear and concise notation facilitates easy communication and minimizes the risk of errors.
Benefits of using standardized metric steel sizes include: 1) Reduced material waste due to precise dimensions, 2) Improved structural integrity through predictable performance, and 3) Enhanced international collaboration facilitated by a common measurement language.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Metric Steel Sizes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Global compatibility | Potential for conversion errors from imperial systems |
| Simplified design and fabrication | Limited availability of certain non-standard sizes |
| Reduced material waste | Initial learning curve for those unfamiliar with the metric system |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the most common metric steel sizes? - This depends on the application, but common sizes include I-beams, angles, channels, and hollow sections with varying dimensions.
2. Where can I find a table of standard metric steel sizes? - Many steel suppliers and industry organizations provide comprehensive tables and resources.
3. How do I convert imperial steel sizes to metric? - Online converters and conversion tables are readily available.
4. What are the tolerances for metric steel sizes? - Tolerances are defined by relevant standards and vary depending on the type of steel and its application.
5. What are the different grades of metric steel? - Steel grades are categorized based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties.
6. How are metric steel sizes designated? - Typically by their cross-sectional dimensions and thickness, e.g., 100 x 50 x 5 mm.
7. Where can I learn more about metric steel design? - Numerous textbooks, online courses, and industry publications offer comprehensive information on metric steel design principles.
8. What are the key considerations when selecting metric steel sizes for a project? - Factors include load requirements, structural design, and material availability.
In conclusion, the adoption of standardized key steel sizes in the metric system has revolutionized the construction and manufacturing industries. From enabling efficient global collaboration to ensuring structural integrity and minimizing material waste, the benefits are undeniable. While challenges such as accurate conversion and familiarity with the metric system exist, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks. By embracing these standardized dimensions, we contribute to a more efficient, sustainable, and interconnected world. Understanding and utilizing these standards is not merely a technical necessity; it’s an essential step towards building a future where precision and collaboration are the cornerstones of progress. The next time you encounter a steel structure, take a moment to appreciate the silent language of standardized metric sizes, the invisible framework that supports our modern world. It's a testament to human ingenuity and our collective pursuit of precision and efficiency.
Woodruff Key Size Chart Metric - Trees By Bike
Printable Socket Size Chart Metric And Standard - Trees By Bike
standard key steel sizes metric - Trees By Bike
Keyway Shaft Size Chart - Trees By Bike
standard key steel sizes metric - Trees By Bike
Keyway Shaft Size Chart - Trees By Bike
Free CAD Designs Files 3D Models - Trees By Bike
Standard Inch Keyway Dimensions Chart - Trees By Bike
Allen Key Size For Tap at Julia Tyler blog - Trees By Bike
Shaft Key Catalogue at John Nail blog - Trees By Bike
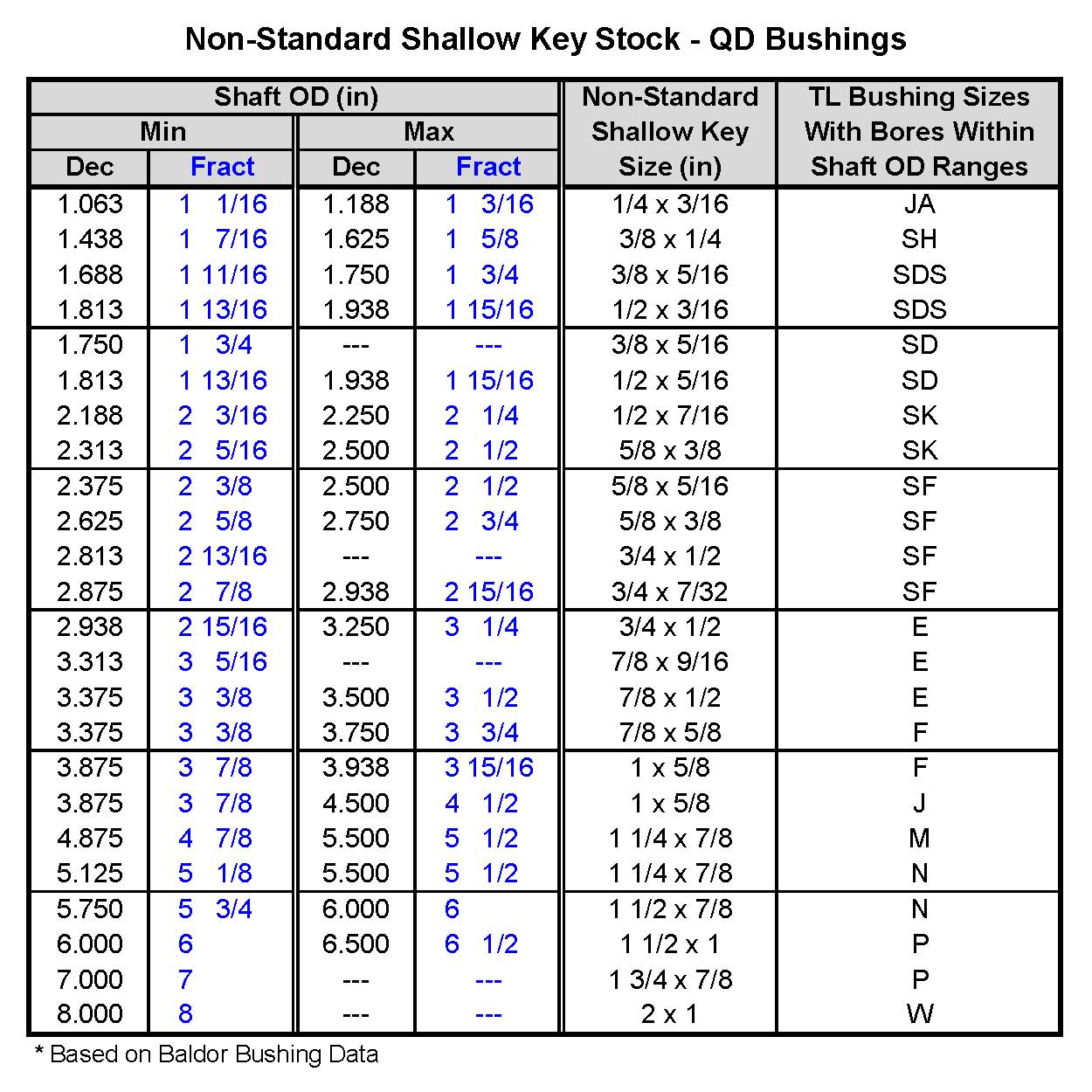
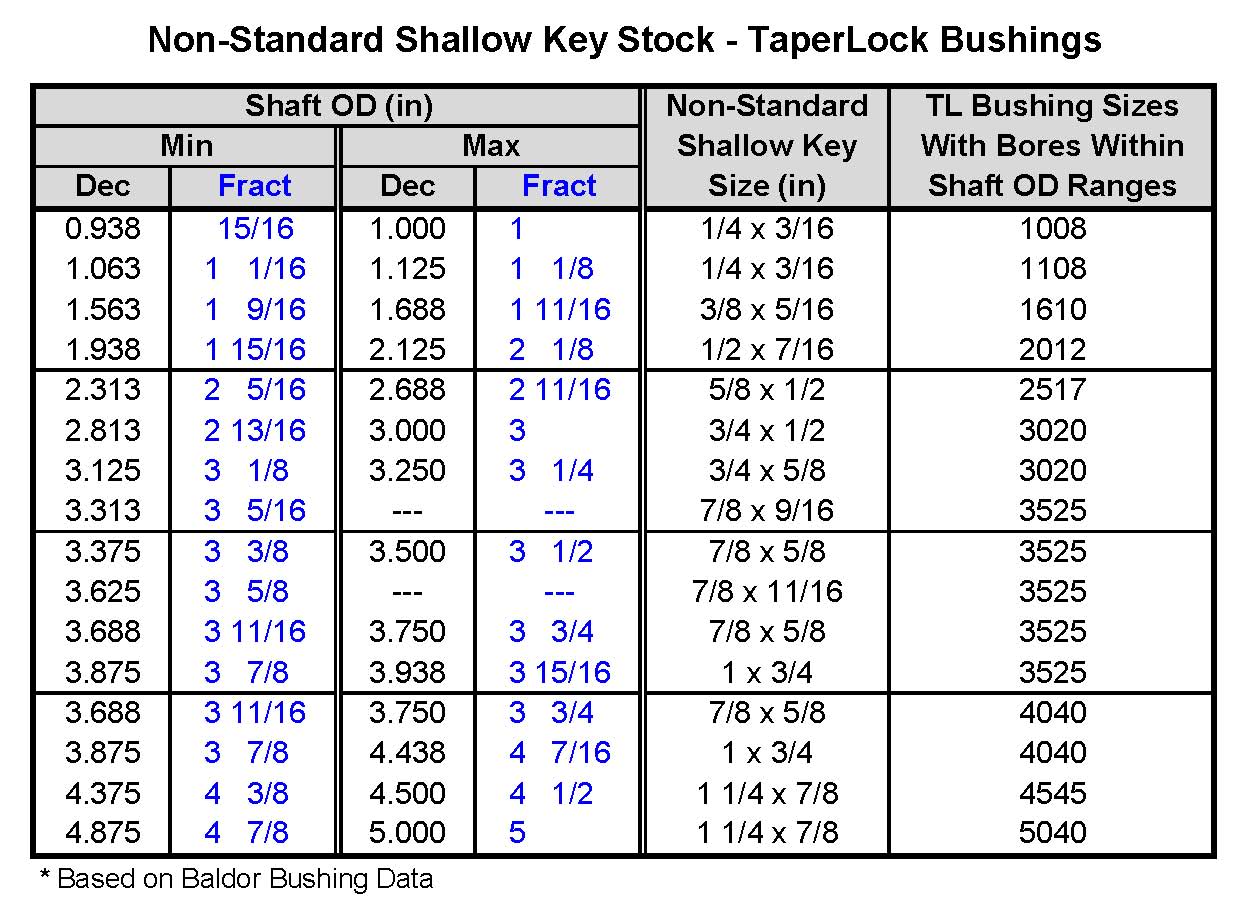
Rectangular Key Stock Sizes - Trees By Bike
Torque Converter Size Calculator at Marshall Sierra blog - Trees By Bike
Bolt Tightening Torque Chart - Trees By Bike
Metric Keyway Tolerance Chart - Trees By Bike
Drive Shaft Key Sizes at Earl Surrett blog - Trees By Bike