Ever wondered about the colored wires snaking through your walls? Understanding the roles of these colored conductors, particularly the green, black, and white wires, is crucial for electrical safety and proper functioning of your home's electrical system. This article delves into the world of electrical wiring, focusing on the significance of these three key colors.
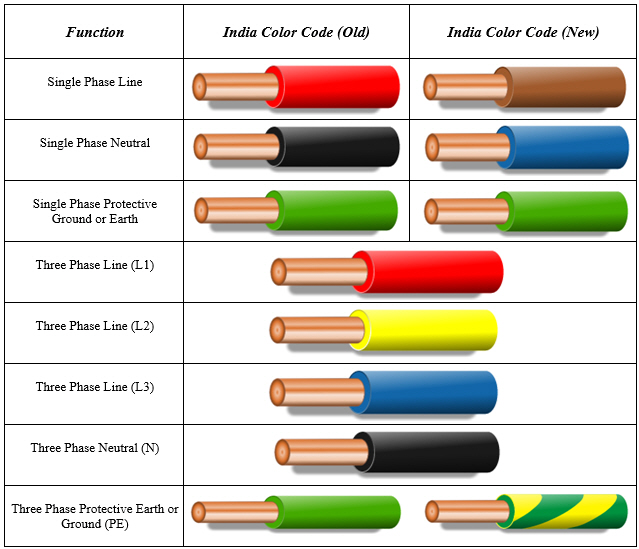
Electrical wiring color codes provide a universal language for electricians, ensuring consistency and safety in installations. While different regions may have slight variations, the fundamental principles remain constant. In North America, the green wire represents the grounding path, the black wire typically carries the hot or live current, and the white wire serves as the neutral conductor.
The origins of color-coded electrical wiring can be traced back to the early 20th century as the need for standardization in electrical installations became increasingly apparent. Harmonizing color schemes minimized confusion and promoted safer practices. The established color codes allow for quick identification of wire function, simplifying troubleshooting and reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
The importance of correctly identifying and connecting green, black, and white electrical wires cannot be overstated. Improper wiring can lead to electrical shocks, short circuits, and even fires. A thorough understanding of these color codes is paramount for anyone working with electrical systems, from professional electricians to DIY enthusiasts.
Misinterpreting or misconnecting electrical wiring colors poses significant risks. Connecting a hot wire to a neutral or ground wire can create a dangerous electrical fault. Understanding the function of each wire color is fundamental for preventing such hazards and ensuring the safety of your home and its occupants.
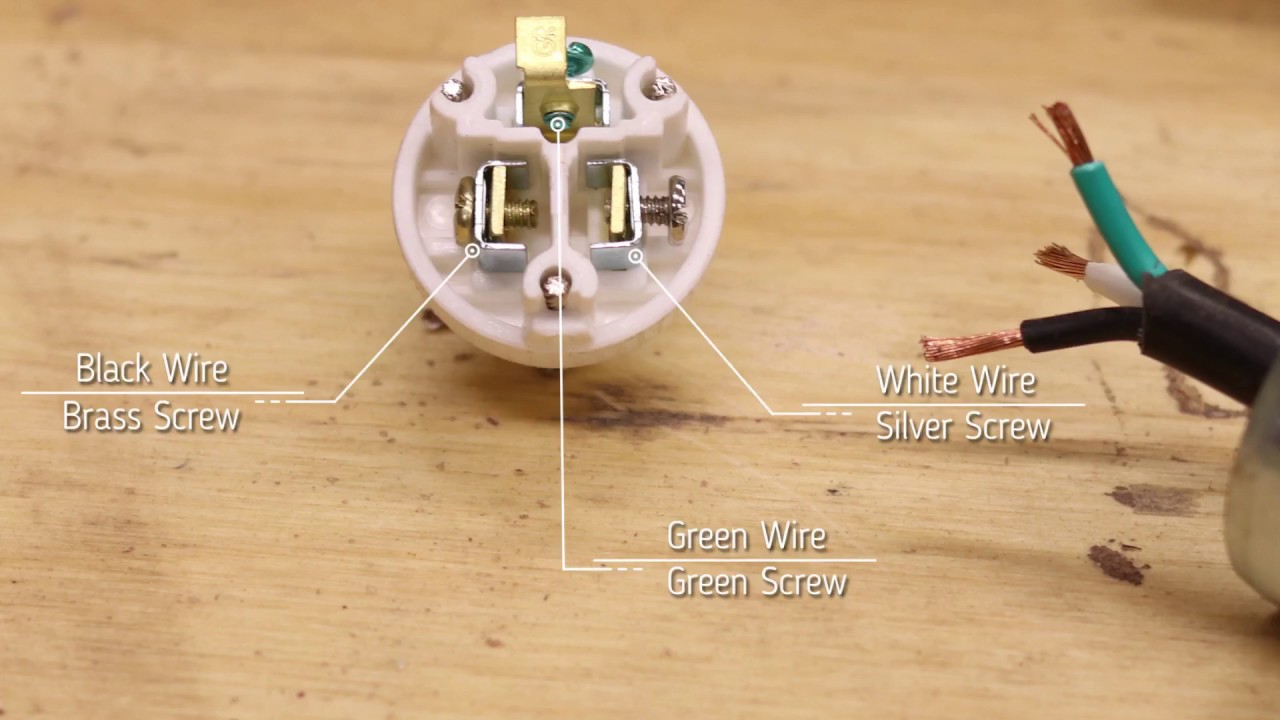
The green wire, universally recognized as the ground wire, provides a safe path for stray electrical currents to flow back to the earth, protecting individuals and equipment from electrical shocks. The black wire, commonly referred to as the hot wire, carries the current from the power source to electrical devices. The white wire, or neutral wire, completes the circuit by providing a return path for the current back to the source after it has passed through the device.
Correctly connecting the green grounding wire is crucial for electrical safety. It ensures that any fault current is safely diverted to the earth, preventing dangerous voltage buildup on metal enclosures. Properly connecting the black and white wires ensures the correct flow of electricity, powering devices efficiently and safely.
One real-world example is a standard lighting fixture. The black wire brings the electrical current to the light bulb, the white wire provides the return path, and the green wire grounds the fixture's metal parts. Another example is in a typical household outlet where the black wire feeds the hot side of the outlet, the white wire connects to the neutral side, and the green wire connects to the grounding terminal.
A challenge in older homes can be the absence of a green ground wire. The solution is to retrofit a grounding system or use a GFCI outlet for enhanced safety. Another challenge might be identifying wires in older installations where the insulation may have faded or become brittle. In such cases, a non-contact voltage tester can help identify live wires.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Color-Coded Wiring
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety | Color Blindness Issues |
| Simplified Troubleshooting | Potential for Fading/Deterioration |
| Standardized Installations | Regional Variations |
Best Practices for Electrical Wiring:
1. Always turn off the power at the breaker box before working on any electrical wiring.
2. Use wire strippers to carefully remove insulation without damaging the conductor.
3. Use appropriately sized wire nuts to secure connections.
4. Ensure all connections are tight and secure.
5. Regularly inspect wiring for damage or deterioration.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What does the green wire do? It provides a grounding path for safety.
2. What does the black wire do? It carries the hot or live current.
3. What does the white wire do? It serves as the neutral conductor.
4. Why is proper wiring important? It ensures safety and prevents electrical hazards.
5. What should I do if I encounter damaged wiring? Contact a qualified electrician.
6. Can I work on electrical wiring myself? If you are unsure, consult a professional.
7. What tools do I need for basic electrical work? Wire strippers, screwdrivers, and wire nuts are essential.
8. Where can I learn more about electrical wiring? Consult local electrical codes and seek guidance from licensed electricians.
Tips and Tricks: Always double-check your work and never hesitate to consult a qualified electrician if you are unsure about any aspect of electrical wiring.
In conclusion, understanding the function and importance of green, black, and white electrical wires is fundamental for ensuring electrical safety and the proper operation of your home's electrical system. Correctly identifying and connecting these wires is crucial for preventing electrical hazards and ensuring the longevity of your electrical devices. While this article provides a comprehensive overview, consulting local electrical codes and seeking guidance from licensed electricians is always recommended for any electrical work. Remember, prioritizing safety is paramount when dealing with electricity. Take the time to learn and understand the fundamentals of electrical wiring – it's an investment in the safety and well-being of your home and its occupants. Don't take chances with electricity; make informed decisions and prioritize safety above all else. Your understanding and diligence can prevent accidents and ensure a safe and functional electrical system in your home. If you have any doubts or concerns, consulting a qualified electrician is always the best course of action.
Extension Cord Ground Plug - Trees By Bike
Extension Cord Hot And Neutral Wires - Trees By Bike
Electrical Wiring Red Black White - Trees By Bike
Electrical Colour Codes Australia - Trees By Bike
What Is White Wire In Electrical - Trees By Bike
Ac Wiring Colors Green Black White - Trees By Bike
Black Wire And White Wire On Light Switch - Trees By Bike
Electrical Wiring Black And White Wires - Trees By Bike
How To Wire A 2 Wire Plug - Trees By Bike
Electrical Wire Color Codes - Trees By Bike
Standard Electrical Outlet Colors at James Rankins blog - Trees By Bike
Electrical Wiring Black And Red - Trees By Bike
Colour Coding For Electrical Wiring - Trees By Bike
Electrical Wiring Colors Red Black White - Trees By Bike
Black And White Wire In Extension Cord at Jason Hammonds blog - Trees By Bike



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SPR_1152863-electrical-wire-color-coding-5afca004fa6bcc0036b72fd5.png)






/ElectricalWiring_FINAL2-5c01dc0546e0fb0001f4d760.png)

