Navigating the complexities of federal government employment involves understanding its unique compensation structure. One crucial aspect is the step increase system, a structured approach to salary advancement within a specific pay grade. This system aims to reward employees for consistent performance and continued service, providing a clear path for financial growth throughout their federal careers. But how exactly does it work, and what factors influence the timing and amount of these increases?
The federal government step increase time period, often referred to as within-grade increases (WGIs), is a predetermined timeframe an employee must serve at a particular step within their grade before becoming eligible for a salary increase to the next step. This period typically involves waiting a specific number of years, often one, two, or three, depending on the step and the applicable pay system, such as the General Schedule (GS). These increases are distinct from promotions, which involve moving to a higher grade and often require competitive selection processes.
The history of the federal government's structured pay system dates back decades, aiming to create a fair and transparent compensation framework. The step increase system emerged as a key component, providing a mechanism for recognizing employees' continued service and performance. It offers predictability and incentivizes employees to remain within the federal workforce, fostering stability and experience within government agencies. This predictable progression allows federal employees to anticipate future earnings and plan their financial futures accordingly.
Understanding the federal government step increase time period is crucial for several reasons. First, it allows employees to accurately project their future income. Second, it encourages employee retention by offering regular salary advancements. Third, it contributes to a standardized compensation structure across the federal government, promoting fairness and transparency. However, there can be complexities related to step increases. For instance, certain performance issues or disciplinary actions could potentially delay or even forfeit an employee's eligibility for a step increase.
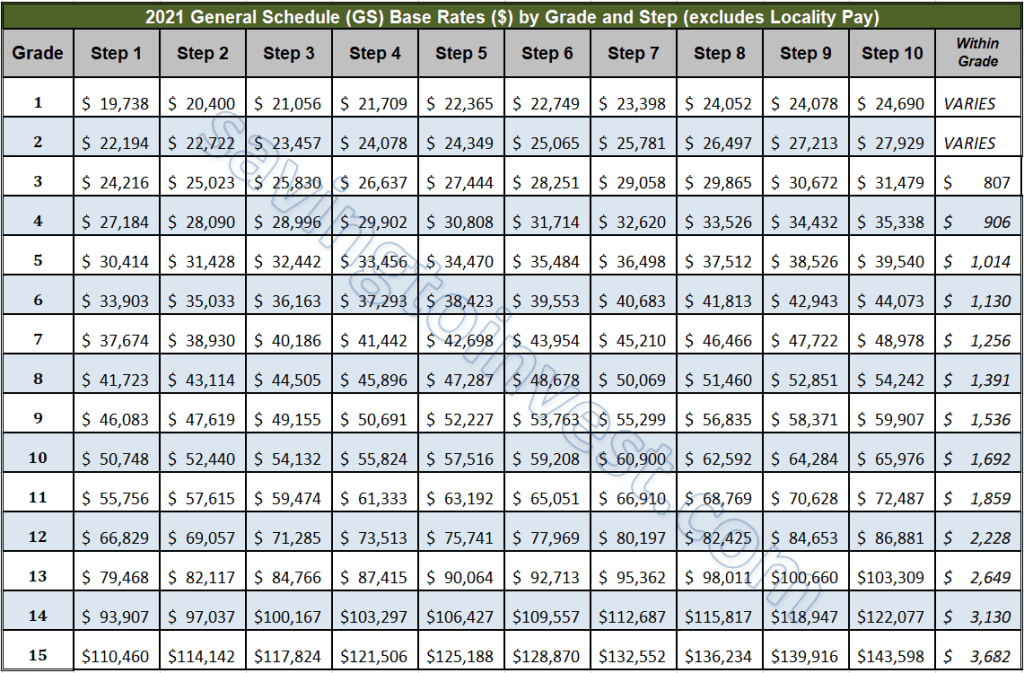
A within-grade increase represents a salary bump within an employee's current General Schedule (GS) grade and step. For instance, a GS-9, Step 5 employee, after fulfilling the required waiting period, would advance to GS-9, Step 6, receiving a higher salary. The specific salary amounts for each grade and step are readily available in published pay tables. For example, if the waiting period is two years, the employee would need to perform satisfactorily for two years at Step 5 before becoming eligible for Step 6. This mechanism provides a clear path for salary growth based on consistent performance and tenure.
Three key benefits of the federal government step increase time period include: Predictable income growth, improved employee morale and retention, and standardized compensation across agencies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Federal Government Step Increases
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable salary growth | Can be perceived as slow advancement |
| Incentivizes employee retention | Limited flexibility in rewarding exceptional performance outside of standard increases |
| Standardized compensation | May not adequately reflect market value for certain in-demand skills |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a within-grade increase? (A: A salary increase within your current grade.)
2. How long is the typical waiting period? (A: Often one, two, or three years, depending on the step.)
3. What can affect my eligibility? (A: Performance and disciplinary actions.)
4. Where can I find the pay tables? (A: OPM website.)
5. Are step increases automatic? (A: Generally, yes, assuming satisfactory performance.)
6. What is the difference between a step increase and a promotion? (A: Step increase is within your grade, promotion is to a higher grade.)
7. Can my step increase be denied? (A: Yes, due to performance issues.)
8. How do I learn more about my agency's specific policies? (A: Consult your HR department.)
Tips and Tricks: Monitor your performance evaluations and stay informed about your agency’s specific policies regarding within-grade increases.
In conclusion, the federal government step increase time period is a fundamental component of the federal compensation system. While it offers predictable salary growth, encourages retention, and standardizes compensation across agencies, it's important to understand the nuances of this system, including eligibility criteria and potential influencing factors. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you can effectively manage your career progression and financial future within the federal government. Understanding the rules, timelines, and potential impacts of this system empowers federal employees to plan their careers and maximize their earning potential within the structured environment of government service. Take the time to review the available resources, discuss any questions with your human resources department, and proactively manage your performance to ensure timely and consistent salary advancements.
federal government step increase time period - Trees By Bike
Gs Schedule 2024 San Francisco - Trees By Bike
2017 Pay Raise Approved for Federal Employees on GS Pay Scale - Trees By Bike
Gs Pay Scale 2024 Step Increases - Trees By Bike
federal government step increase time period - Trees By Bike
Federal Pay Raise 2024 Washington Dc - Trees By Bike
Why It Is Time to Reform Compensation for Federal Employees - Trees By Bike
pay scale chart 2017 federal government Expected revised pay scale - Trees By Bike
Gs 15 Pay Scale Dc 2023 - Trees By Bike
Federal Pay Scale Increase 2023 - Trees By Bike
Federal Government Releases New Salary Table - Trees By Bike