Imagine stepping into your backyard and harvesting fresh, flavorful vegetables you nurtured from tiny seeds. This dream can easily become a reality with the right guidance, even in Zone 6's unique climate. This comprehensive guide provides everything you need to know about planning, planting, and nurturing a thriving vegetable garden tailored to the specific challenges and opportunities of Zone 6.
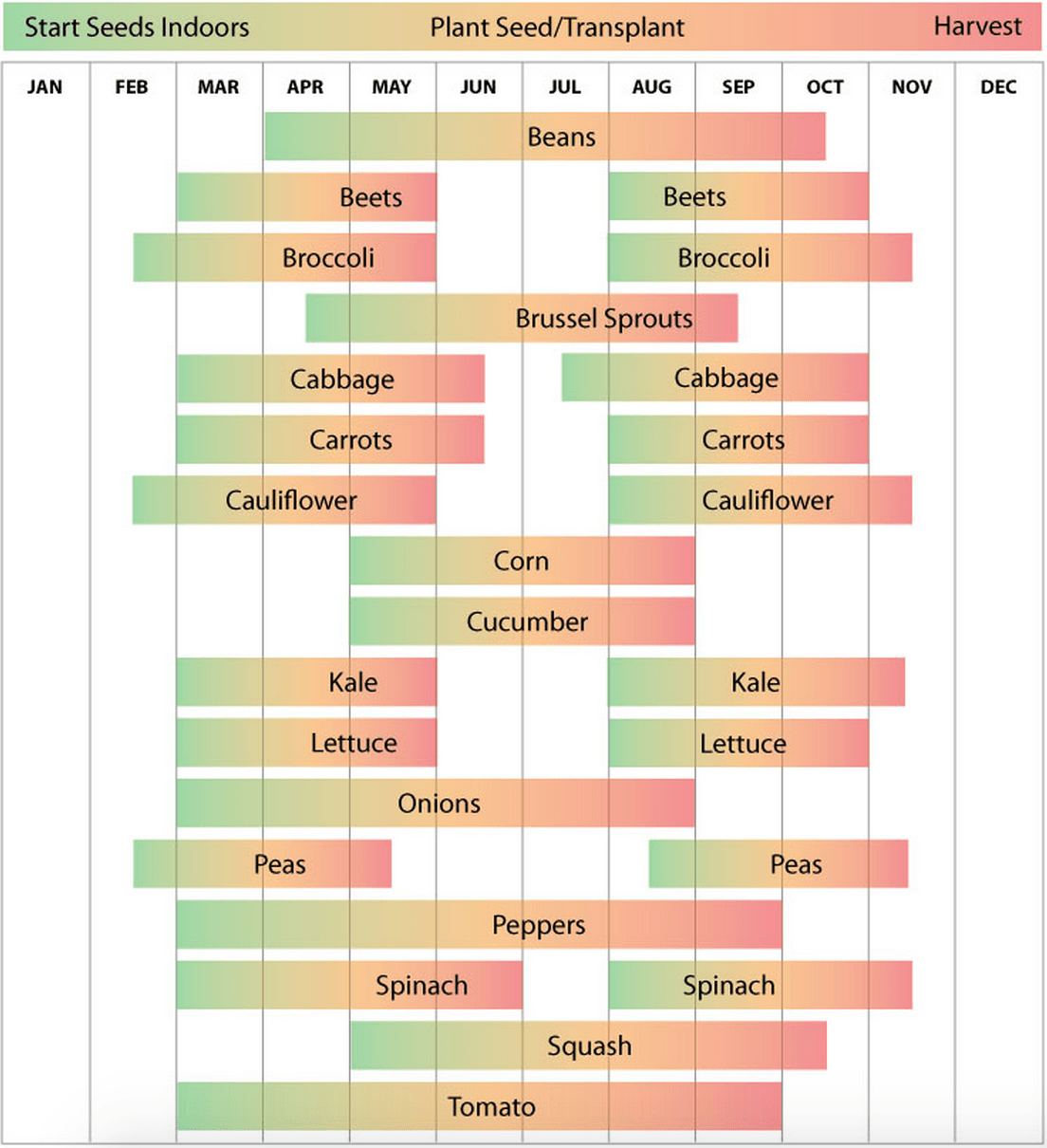
Zone 6 gardening presents a unique set of considerations. Characterized by moderate winters and summers, with an average first frost date between October 1st and 15th and last frost between April 1st and May 15th, this zone requires careful crop selection and timing. Successfully navigating these seasonal shifts is key to a bountiful harvest.
While the specifics of vegetable gardening have evolved with modern techniques and technology, the fundamental principles remain rooted in historical practices. For generations, gardeners have adapted their methods to their local climate and soil conditions, developing a wealth of knowledge passed down through time. Understanding these basic principles, alongside modern innovations, is crucial for Zone 6 success.
A well-planned Zone 6 vegetable garden offers significant rewards beyond the satisfaction of nurturing your own food. Freshly harvested vegetables are often richer in nutrients and flavor compared to store-bought produce. Gardening also offers a connection to nature, providing a relaxing and rewarding hobby that promotes physical activity and reduces stress. Moreover, growing your own vegetables contributes to sustainable living by reducing food miles and supporting local ecosystems.
One of the primary challenges in Zone 6 gardening is the relatively shorter growing season compared to warmer zones. This necessitates careful planning and the selection of varieties suited to these conditions. Understanding frost dates, utilizing season-extending techniques, and implementing proper soil preparation are vital for maximizing your yield.
Understanding your "last frost date" is essential. This is the average date of the last spring frost in your area. Planting too early risks frost damage to tender seedlings. Conversely, planting too late shortens the growing season. Consult local resources or online tools to pinpoint your area's last frost date.
Three key benefits of utilizing a Zone 6 vegetable gardening guide are informed plant selection, optimized planting schedules, and improved harvest yields. By selecting varieties specifically adapted to the Zone 6 climate, like cold-hardy greens and quick-maturing tomatoes, you'll maximize your chances of success. An optimized planting schedule ensures that you start seeds indoors at the right time and transplant them outdoors when the weather is favorable. These practices ultimately lead to a healthier, more abundant harvest.
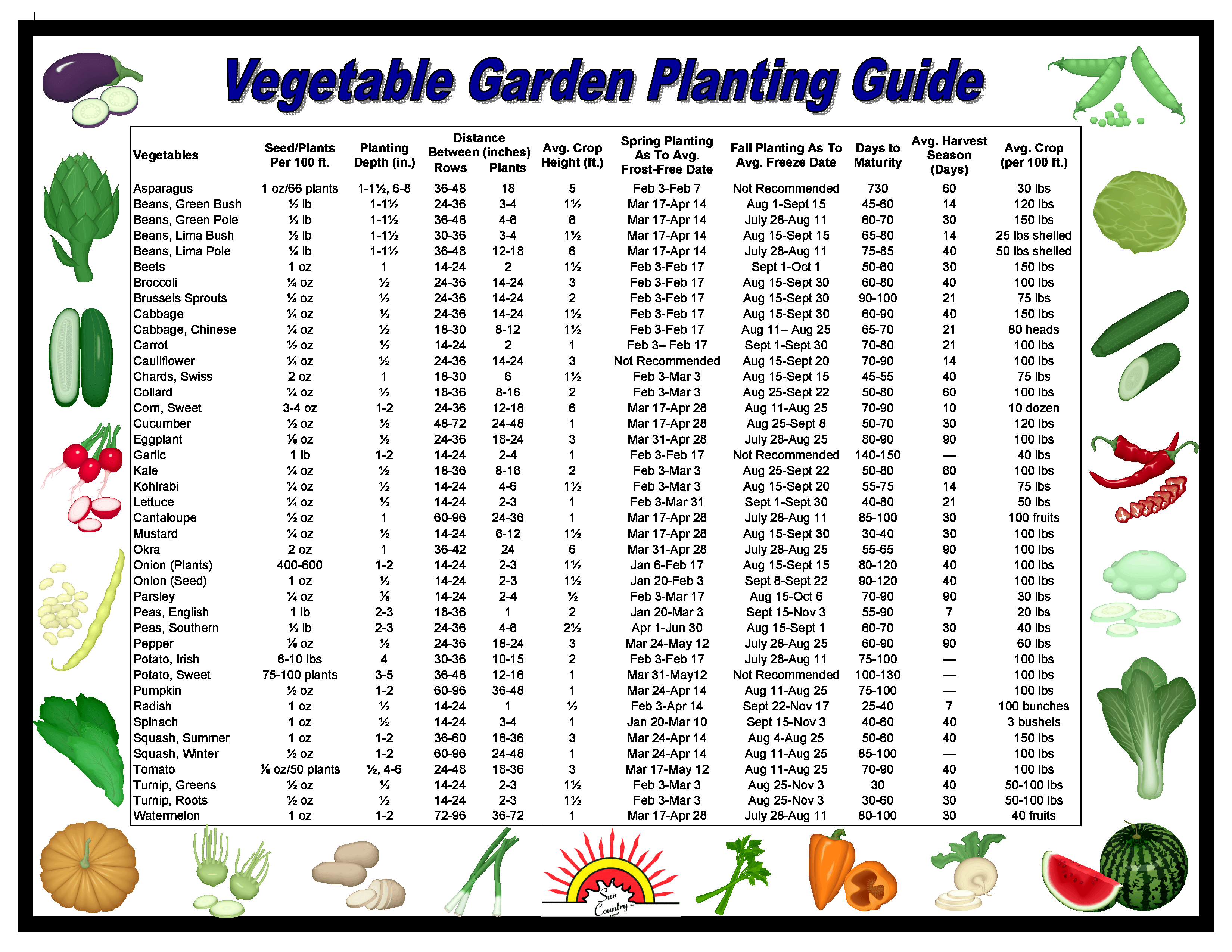
Your Zone 6 gardening journey begins with planning. Determine your garden location, ensuring ample sunlight. Next, test your soil and amend it as needed. Choose vegetable varieties suitable for Zone 6 and create a planting schedule based on your last frost date. Start seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before the last frost for crops like tomatoes and peppers. Finally, harden off your seedlings before transplanting them outdoors.
A step-by-step guide can include: 1) Soil Preparation: Test and amend your soil for optimal nutrient levels. 2) Seed Starting: Begin seeds indoors according to your planting schedule. 3) Hardening Off: Gradually acclimate seedlings to outdoor conditions before transplanting. 4) Transplanting: Plant seedlings in prepared garden beds after the last frost. 5) Watering: Provide consistent watering, especially during dry periods. 6) Fertilizing: Supplement nutrients as needed throughout the growing season. 7) Pest and Disease Control: Implement preventative measures and address any issues promptly. 8) Harvesting: Harvest vegetables at their peak ripeness for optimal flavor and nutrition.
Resources like the Farmer's Almanac and local extension offices provide valuable information specific to your region. Many mobile apps offer planting calendars and reminders tailored to your zone.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zone 6 Gardening
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enjoy a wide variety of vegetables | Shorter growing season than warmer zones |
| Moderate climate allows for extended harvests | Risk of late spring and early fall frosts |
| Distinct four seasons provide opportunities for different crops | Requires careful planning and variety selection |
Five best practices for Zone 6 vegetable gardening: 1) Choose appropriate varieties. 2) Start seeds indoors. 3) Protect plants from frost. 4) Water and fertilize regularly. 5) Practice crop rotation.
Examples of successful Zone 6 gardens often include cold-hardy leafy greens, root vegetables like carrots and beets, and quick-maturing varieties of warm-season crops like tomatoes and peppers.
Common challenges include late frosts, pests, and diseases. Solutions involve using row covers, implementing integrated pest management strategies, and choosing disease-resistant varieties.
FAQs: What vegetables grow best in Zone 6? When should I start seeds indoors? How do I protect my plants from frost? What are common Zone 6 pests? How do I amend my soil? When should I harvest my vegetables? What are good companion planting strategies for Zone 6? How do I extend my growing season?
Tips: Utilize raised beds for improved drainage and soil warming. Employ companion planting to deter pests and enhance growth. Extend your season with row covers and cold frames.
Growing your own vegetables in Zone 6 is a rewarding endeavor. By understanding the specific needs of this climate, from frost dates to suitable varieties, you can transform your backyard into a thriving source of fresh, nutritious food. This guide has provided the foundation for your Zone 6 gardening journey, equipping you with the knowledge and resources to cultivate a successful and abundant harvest. From planning and planting to ongoing care and eventual harvest, each step plays a crucial role in achieving your gardening goals. Embrace the process, learn from your experiences, and savor the fruits (and vegetables!) of your labor. Start your Zone 6 garden today and experience the joy of homegrown goodness.
A3 novice allotment planner gardenersbeginners vegetable growing - Trees By Bike
Planting Calendar For Zone 7a - Trees By Bike
When To Plant A Vegetable Garden In Michigan at Katherine Green blog - Trees By Bike
Vegetable Garden Plans Zone 6 at Edward Erhart blog - Trees By Bike
Vegetable Planting Guide Zone 6 - Trees By Bike
Companion Planting For Garbanzo Beans at Michael Prince blog - Trees By Bike
What Can I Plant Now In Nj at April Padro blog - Trees By Bike
Zone 8A Vegetable Planting Calendar - Trees By Bike
Veggies To Grow In Garden at Matthew Theus blog - Trees By Bike
What Is The Growing Zone For Ohio at Deborah Staggs blog - Trees By Bike
vegetable growing guide for zone 6 - Trees By Bike
When Should I Plant What - Trees By Bike
Understanding Perennial Zones A Guide To Sustainable Gardening And - Trees By Bike
What Vegetables To Plant In Summer In Brisbane at Marilyn Medellin blog - Trees By Bike
Vegetable Planting Calendar Missouri - Trees By Bike