Imagine a world where machines could sense objects without physical contact. A world where automated systems seamlessly react to the presence or absence of something nearby. That world, my friends, is powered by the often-unsung hero of automation: the proximity switch. But the world of prox switches isn't a one-size-fits-all affair. Let's embark on a journey to understand the fascinating variations within the realm of proximity switch types.
Proximity switches, often abbreviated as prox switches, are electronic sensors that detect the presence of nearby objects without requiring physical contact. Think of them as the watchful eyes of industrial automation, constantly monitoring and triggering actions based on the proximity of objects. These remarkable devices are the backbone of countless automated processes, from simple conveyor belt systems to complex robotic assembly lines. Understanding the various proximity switch varieties is crucial for harnessing their full potential and optimizing automation strategies.
The history of prox switches is interwoven with the rise of industrial automation. Early mechanical limit switches, with their inherent limitations, paved the way for the development of non-contact sensing solutions. The need for more reliable, faster, and adaptable sensing mechanisms fueled the innovation that led to the different types of proximity switches we see today. From inductive prox switches, designed to detect metallic objects, to capacitive prox switches capable of sensing a wider range of materials, each variation emerged to address specific automation challenges.
The significance of prox switch types lies in their versatility and adaptability to various industrial applications. Choosing the correct prox switch category is paramount for achieving efficient and reliable automation. Factors like the target material, operating environment, and sensing range play a critical role in selecting the appropriate switch. For instance, an inductive proximity switch is ideal for detecting metal objects in a harsh industrial environment, while a capacitive prox switch might be better suited for sensing the presence of liquids or non-metallic materials.
A key challenge in using different prox switch classifications lies in understanding their unique operating principles and limitations. For example, inductive prox switches are susceptible to interference from electromagnetic fields, while capacitive prox switches can be affected by environmental factors like temperature and humidity. Recognizing these potential issues is crucial for troubleshooting and ensuring reliable operation.
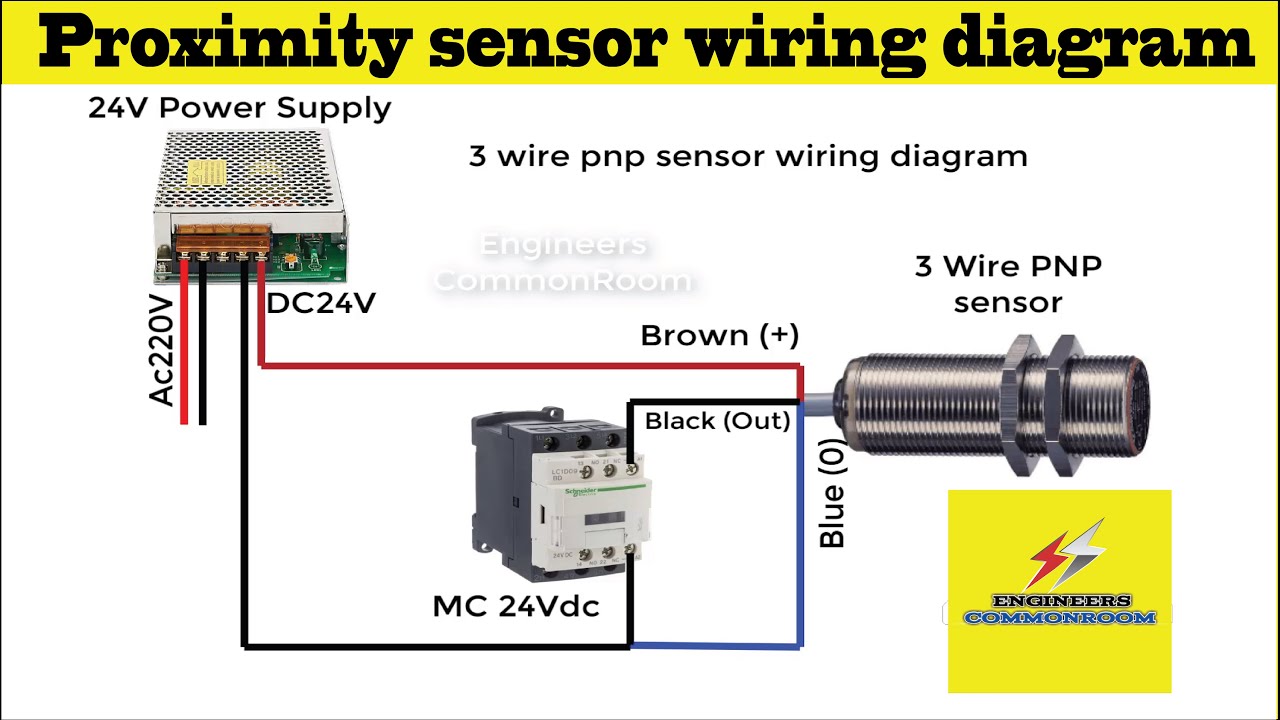
Inductive proximity switches operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They generate a magnetic field and detect changes in that field caused by the presence of a metallic object. Capacitive proximity switches, on the other hand, create an electric field and detect variations in capacitance caused by the proximity of any material that influences the field.
Benefits of using prox switches include increased automation efficiency, improved safety, and reduced maintenance. For instance, in a bottling plant, prox switches can detect the presence of bottles and trigger filling mechanisms, ensuring seamless and automated operation.
When implementing prox switches, consider factors like sensing range, target material, and environmental conditions. Choose the appropriate prox switch type based on your specific application requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Proximity Switch Types
(Table would be inserted here with different types, their advantages, and disadvantages)
Best practices include proper mounting, wiring, and configuration of the prox switches according to the manufacturer's specifications.
Real-world examples include: bottle filling lines, conveyor belt systems, robotic welding, automated doors, and level detection in tanks.
Challenges can include environmental interference, incorrect installation, and sensor malfunction. Solutions include proper shielding, calibration, and regular maintenance.
FAQs: What is a prox switch? How does it work? What are the different types? How to choose the right one? How to install? How to troubleshoot? What are the applications? What are the benefits?
Tips and tricks: Regularly check for damage, ensure proper grounding, and consider environmental factors.
In conclusion, proximity switches are indispensable components in modern automation systems. Understanding the diverse types of prox switches, their applications, and best practices is paramount for optimizing automation processes and maximizing efficiency. From simple presence detection to complex robotic control, these versatile sensors play a vital role in shaping the future of industrial automation. By carefully considering the specific needs of each application and selecting the appropriate prox switch category, engineers and technicians can unlock the full potential of these remarkable devices and pave the way for smarter, safer, and more efficient automation solutions. Embracing the power of proximity sensing technology is crucial for staying competitive in today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape. Explore the world of prox switches further and discover the endless possibilities they offer.
3 Wire Proximity Sensor Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike
What Is A Proximity Switch - Trees By Bike
Prox Switch Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike
Ac Proximity Sensor Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike
Proximity Sensor Wiring Diagram and Connection Procedure - Trees By Bike
An Easy Way to Remember PNP and NPN Sensor Wiring - Trees By Bike
Samostan podzemna željeznica Obično all types of switches tunel - Trees By Bike
medallista Gracias Para un día de viaje sensor proximidad raspador - Trees By Bike
Proximity Sensor 2 Wire Connection - Trees By Bike
types of prox switches - Trees By Bike
Inductive Proximity Sensor Wiring Diagrams - Trees By Bike
4 Wire Proximity Sensor Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike
types of prox switches - Trees By Bike
4 Pin Type Proximity Switches at Rs 650piece - Trees By Bike
3 Wire Proximity Switch Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike