Imagine effortlessly navigating the world of alternating current circuits, simplifying complex calculations with a tool you already own – your calculator. This is the power of understanding phasors. Phasors, a concise way to represent sinusoidal waves, offer an elegant solution to otherwise cumbersome AC circuit analysis. This guide unravels the mystery of phasor calculations, providing you with a clear path to mastering this essential electrical engineering tool.
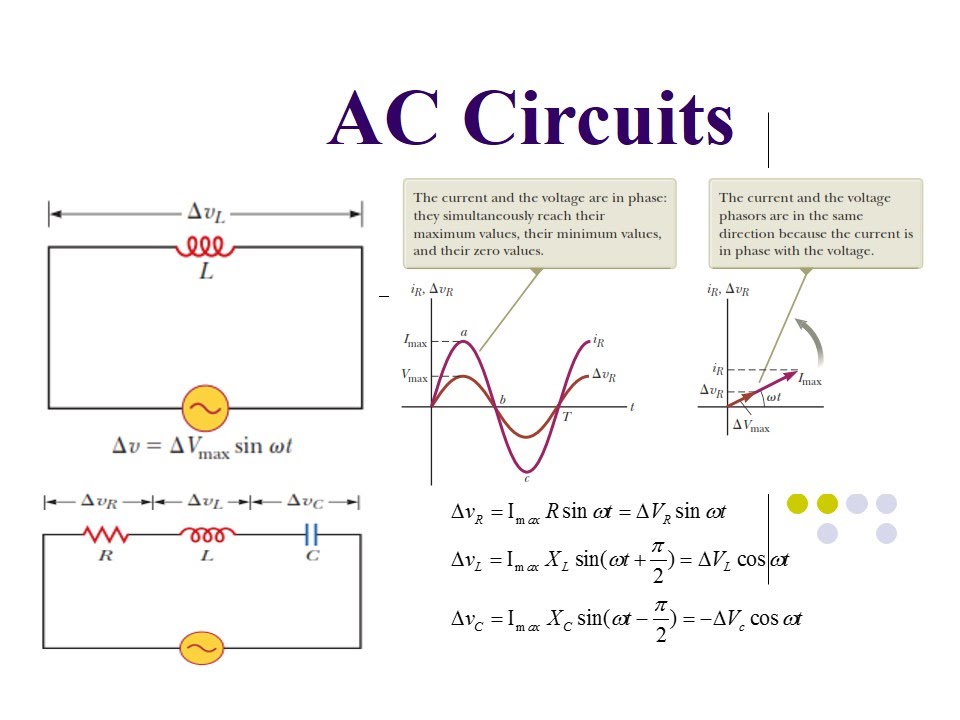
Phasors transform sinusoidal functions, which vary with time, into complex numbers, which are independent of time. This transformation simplifies the process of analyzing AC circuits, allowing us to use algebraic methods instead of differential equations. Instead of grappling with trigonometric functions and their derivatives, we can add, subtract, multiply, and divide complex numbers, making the analysis significantly easier.
The representation of alternating current quantities as phasors has a rich history, stemming from the work of Charles Proteus Steinmetz, a pioneering electrical engineer. Steinmetz's insightful approach provided a vital tool for managing the complexities of AC systems, becoming a cornerstone of electrical engineering education and practice. Before the widespread use of calculators, engineers relied on slide rules and complex number tables to perform phasor calculations. The advent of calculators revolutionized this process, making phasor analysis more accessible and efficient.
One of the primary challenges in working with phasors lies in the correct conversion between the time-domain sinusoidal function and the phasor representation. This involves understanding the amplitude, frequency, and phase of the sinusoidal wave. Mastering this conversion is crucial for accurate phasor calculations and meaningful interpretation of the results. This guide addresses this challenge head-on, providing clear explanations and practical examples.
Understanding phasor calculations is essential for anyone working with AC circuits. Whether you are an electrical engineer, a physics student, or simply curious about the inner workings of electrical systems, the ability to represent and manipulate sinusoidal waves as phasors is a valuable skill. This knowledge opens the door to a deeper understanding of circuit behavior, power analysis, and other key concepts in electrical engineering.
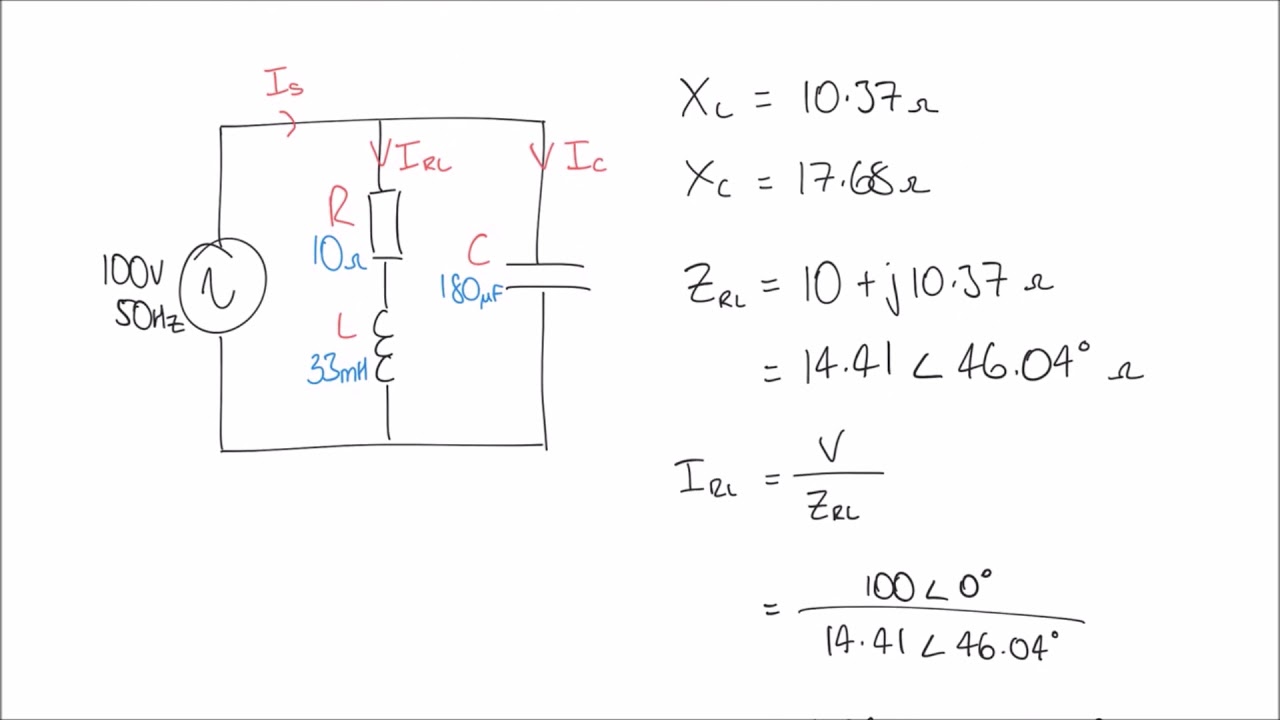
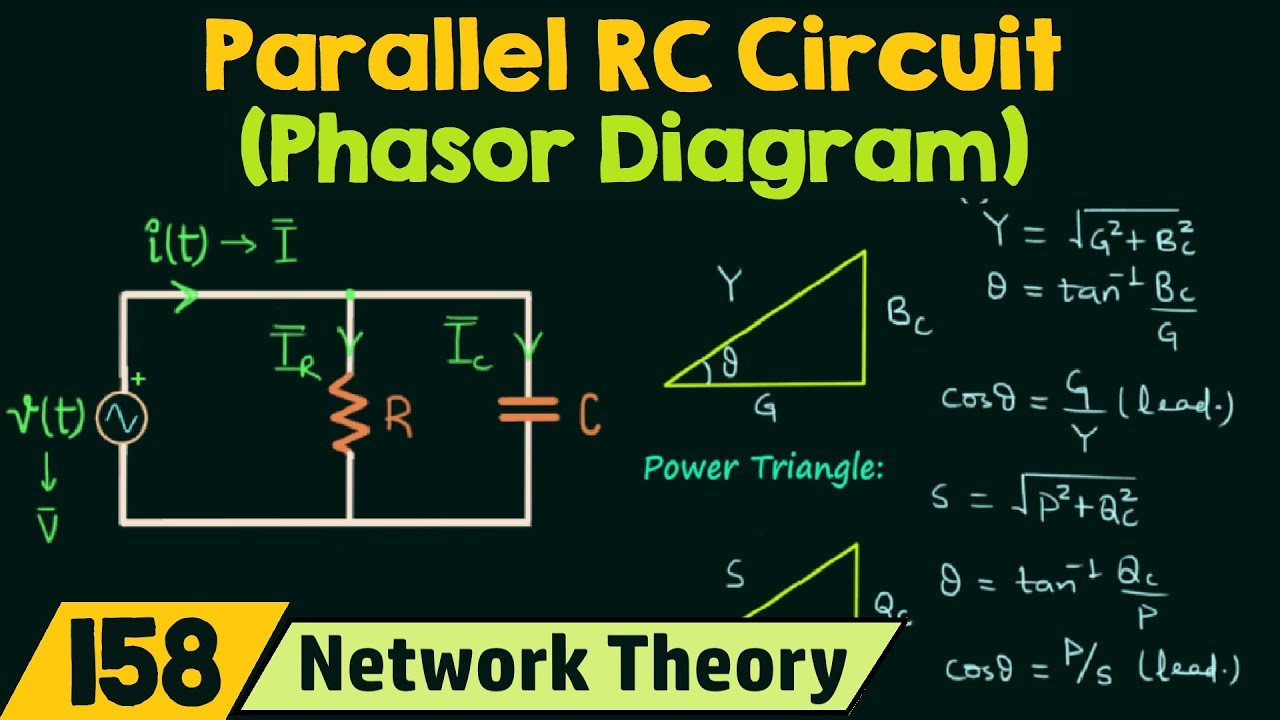
Let's delve into the practical aspects. A phasor is typically represented in two forms: rectangular (a + jb) and polar (A∠θ). 'a' and 'b' represent the real and imaginary components, respectively, while 'A' represents the magnitude and 'θ' the phase angle. Many scientific calculators have built-in functions to convert between these forms. The conversion often involves using trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent) and their inverses, along with the Pythagorean theorem.
Several benefits emerge from using phasors. Firstly, they simplify circuit analysis by replacing differential equations with algebraic operations. Secondly, they provide a clear visual representation of the magnitude and phase relationship between different sinusoidal quantities. Thirdly, they allow for easier analysis of complex circuits with multiple sources and components.
To calculate a phasor in a calculator: 1) Identify the amplitude and phase of the sinusoidal wave. 2) If needed, convert the sinusoidal wave from a trigonometric form to its complex exponential equivalent. 3) Use your calculator's complex number functions (often labeled 'MODE' or 'CMPLX') to convert the complex exponential to either rectangular or polar form.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Calculator-Based Phasor Calculations
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Speed and Efficiency | Potential for Input Errors |
| Automated Conversions | Limited Visualization |
| Handles Complex Numbers Directly | Reliance on Calculator Functionality |
Five Best Practices: 1) Always double-check your input values. 2) Ensure your calculator is in the correct mode (degrees or radians). 3) Understand the limitations of your calculator's precision. 4) Practice with simple examples first. 5) Verify your results with alternative methods if possible.
FAQ: 1) What is a phasor? 2) Why are phasors used? 3) How do I convert between rectangular and polar form? 4) What are the common mistakes in phasor calculations? 5) How are phasors used in AC circuit analysis? 6) How do I represent a sinusoidal wave as a phasor? 7) What is the importance of the phase angle in a phasor? 8) What are the limitations of phasor analysis?
Tips and Tricks: Familiarize yourself with your calculator's complex number functions. Practice converting between different phasor representations. Use online phasor calculators to verify your results.
In conclusion, mastering phasor calculations is a significant step towards understanding and analyzing AC circuits effectively. This guide provides a foundational understanding of phasor representations, calculations, and practical applications. From simplifying complex calculations to providing clear visual representations of sinusoidal waves, the benefits of using phasors are undeniable. By understanding the principles outlined here and practicing regularly, you can harness the power of phasors to unlock a deeper understanding of electrical systems. Embrace the simplicity and efficiency phasors offer and elevate your analytical skills in the world of AC circuits. Start practicing today and witness the transformative power of this elegant mathematical tool.
how to calculate phasor in calculator - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit At Resonance - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit - Trees By Bike
Phase Angle Voltage And Current at Barbara Vega blog - Trees By Bike
Phasor diagram of the modified current phase angle calculation - Trees By Bike
DIAGRAM Single Phase Phasor Diagram - Trees By Bike
Rlc Circuit Phasor Diagram Calculator - Trees By Bike
how to calculate phasor in calculator - Trees By Bike
how to calculate phasor in calculator - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram 3 Phase Ac Circuit - Trees By Bike
how to calculate phasor in calculator - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagrams Of Ac Circuits - Trees By Bike
Three Phase Star Connection Y Three Phase PowerVoltageCurrent - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagrams Of Ac Circuits - Trees By Bike
Rlc Phasor Diagram Calculator - Trees By Bike