Ever glanced at your fuel gauge and wondered how it knows how much gas is in your tank? The answer lies in a small but crucial component: the fuel gauge sending unit, specifically its resistance. This often-overlooked part plays a vital role in keeping you informed about your fuel levels, preventing unexpected stops, and ensuring a smooth driving experience. Understanding how it works can empower you to troubleshoot issues and maintain your vehicle effectively.
The fuel gauge sending unit, sometimes referred to as a fuel level sensor, is a device submerged within the fuel tank. Its primary function is to measure the fuel level and translate it into a resistance value that the fuel gauge can interpret. This resistance changes as the fuel level fluctuates. When the tank is full, the resistance is typically low, and as the fuel level decreases, the resistance increases. This variable resistance is the key to accurate fuel level readings.
The history of fuel level indicators dates back to the early days of automobiles. Early systems were often rudimentary, relying on floats and mechanical linkages to provide a rough estimate of fuel levels. With advancements in technology, the fuel level sender evolved into the more precise and reliable electronic component we know today. The transition to variable resistance-based systems allowed for more accurate readings and integration with electronic dashboards.
The importance of a properly functioning fuel sending unit cannot be overstated. Accurate fuel level readings are essential for planning trips, avoiding running out of gas, and maintaining peace of mind. A faulty fuel sending unit can lead to inaccurate gauge readings, causing unnecessary stress and potentially leaving you stranded on the side of the road. Understanding the role of the sending unit's resistance allows for effective diagnosis and repair of these issues.
One of the most common issues associated with fuel gauge sending units is erratic or inaccurate readings. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including a faulty float, a damaged resistor, or corrosion within the sending unit. Diagnosing these problems often involves testing the sending unit's resistance at different fuel levels. By comparing these readings to the manufacturer's specifications, you can pinpoint the source of the problem and determine the appropriate course of action.
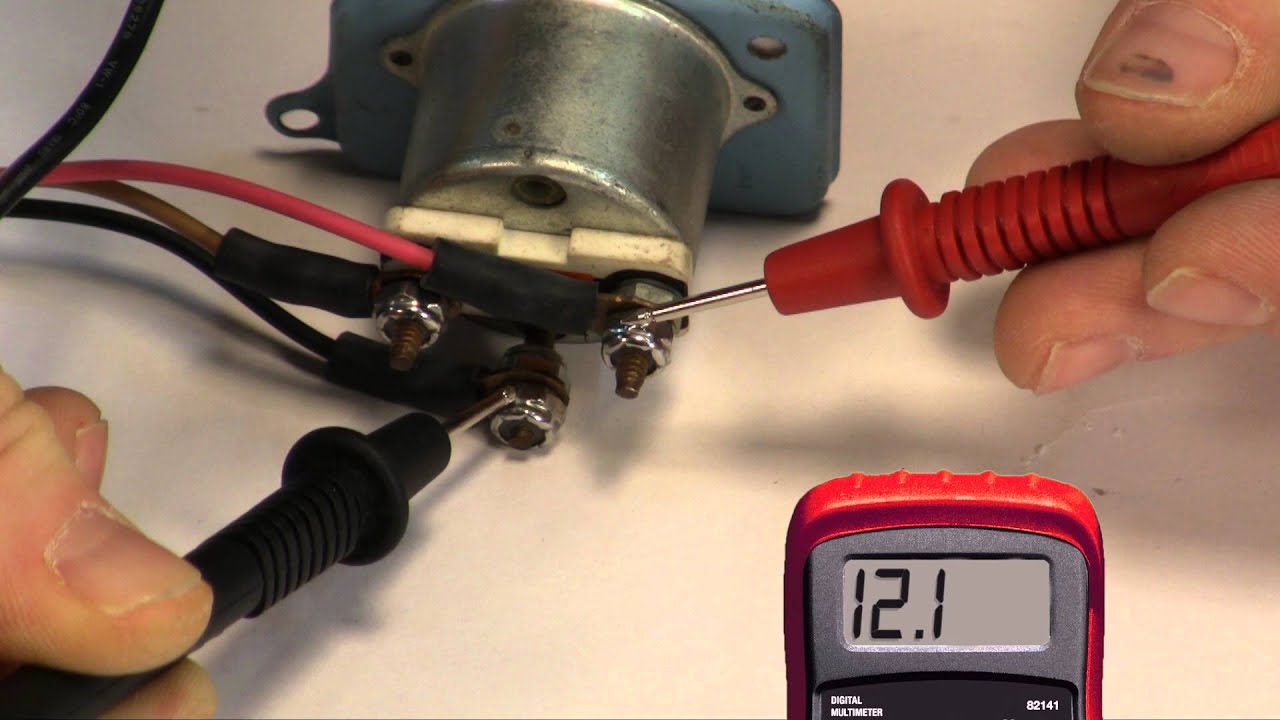
The fuel sending unit resistance is typically measured in ohms. A common range is between 0 ohms (empty) and 90 ohms (full), although this can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. Testing the resistance involves disconnecting the sending unit wiring and using a multimeter to measure the resistance between the appropriate terminals.
One benefit of understanding fuel sender ohms is that you can diagnose issues yourself. For example, if your gauge reads empty but you know you have fuel, you can test the sending unit's resistance. If the resistance is high when the tank is full, the sending unit likely needs replacement.
Another benefit is that you can choose the correct replacement part. Knowing the expected resistance range for your vehicle ensures you purchase a compatible sending unit.
Finally, understanding these principles can help you maintain your vehicle's fuel system. By periodically checking the sending unit's resistance, you can identify potential problems early on and prevent more serious issues from developing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Variable Resistance Fuel Senders
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Relatively simple and cost-effective technology | Susceptible to wear and tear, especially in harsh environments |
| Provides reasonably accurate fuel level readings | Can be affected by fuel contaminants and corrosion |
Troubleshooting a fuel gauge issue often involves checking the sending unit's resistance. A common test is to measure the resistance with a full tank, a half-full tank, and an almost empty tank. Comparing these readings to the vehicle's specifications helps pinpoint the problem.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the typical resistance range for a fuel sending unit? A: It typically varies between 0 ohms (empty) and 90 ohms (full), although this can differ between vehicles.
Q: How do I test a fuel sending unit's resistance? A: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance between the sending unit's terminals.
Q: What causes inaccurate fuel gauge readings? A: Several factors, including a faulty sending unit, wiring issues, or a problem with the gauge itself.
Q: Can I replace a fuel sending unit myself? A: Yes, but it can be a messy job involving working with the fuel tank.
Q: How often should I check my fuel sending unit? A: Periodic checks during regular maintenance can help identify potential problems early.
Q: What are the signs of a failing fuel sending unit? A: Erratic gauge readings, inaccurate fuel level indications, or a gauge that sticks at a certain level.
Q: Where is the fuel sending unit located? A: Inside the fuel tank, usually accessible through an access panel.
Q: What are fuel sender ohms? A: This refers to the resistance of the fuel level sender, which changes based on the fuel level and is used to indicate the amount of fuel in the tank.
Tips and Tricks:
Always consult your vehicle's service manual for specific resistance values and testing procedures.
When working with fuel, take necessary safety precautions, including proper ventilation and disconnecting the battery.
In conclusion, the fuel gauge sending unit and its associated resistance are fundamental components of your vehicle's fuel system. Understanding how these elements work, recognizing potential problems, and knowing how to troubleshoot them can empower you to maintain your vehicle effectively, avoid unexpected breakdowns, and enjoy a smoother driving experience. By paying attention to the subtle cues your fuel gauge provides and understanding the underlying principles of fuel sender ohms, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid the frustration of inaccurate fuel readings. Taking proactive steps to understand and maintain your vehicle's fuel system can save you time, money, and the inconvenience of being stranded with an empty tank. By being informed and proactive, you can ensure accurate fuel readings and maintain control over your vehicle's performance.
Wiring Diagram For Boat Fuel Sending Unit - Trees By Bike
Honda Fuel Gauge Sending Unit at Raymond McFarland blog - Trees By Bike
Chevy Fuel Gauge Ohms - Trees By Bike
Buy 100TECH Marine Fuel Sending Unit Float Replacement 19480mm for - Trees By Bike
Electric Fuel Gauge Wiring Diagram at Russell Summerville blog - Trees By Bike
Fuel Gauge Sender Location at Jack Gilmartin blog - Trees By Bike
Universal Fuel Level Sending Unit for Boats - Trees By Bike
How Does A Sender Unit And Gauge Operate at Francis Wingfield blog - Trees By Bike
fuel gauge sending unit ohms - Trees By Bike
What Is An Oxygen Sensor - Trees By Bike
Fuel Gauge Ohms Chart - Trees By Bike
Fuel Gauge Schematic Diagram - Trees By Bike
John Deere Fuel Sending Unit 0 - Trees By Bike
Temperature Gauge Sender Resistance at Marco Woody blog - Trees By Bike
Boat Fuel Sender Wiring Gauge - Trees By Bike