Have you ever felt overwhelmed by a wall of numbers? Lost in a sea of data, struggling to make sense of it all? Charts offer a lifeline, a visual pathway to understanding complex information quickly and efficiently. They transform raw data into digestible insights, allowing us to grasp trends, patterns, and relationships in a way that words alone simply can't match.
This comprehensive guide will explore the fascinating world of charts in the English language. We'll delve into their history, examine different charting methods, and uncover the secrets to creating compelling visuals that resonate with your audience. From simple bar graphs to intricate network diagrams, charts empower us to tell stories with data, making information accessible and engaging.
The use of visual representations of data, like charts and graphs, has a long and rich history. Early forms of charting can be traced back centuries, with examples found in ancient civilizations. Over time, as the need to analyze and communicate complex data grew, so did the sophistication of charting techniques. The development of statistical methods and the rise of computer technology further propelled the evolution of charting, leading to the diverse array of chart types we have today.
Charts play a crucial role in effective communication, particularly in fields like business, science, and education. They provide a powerful means of presenting data in a clear and concise manner, enabling audiences to quickly grasp key takeaways. Whether you're analyzing sales figures, tracking scientific experiments, or presenting research findings, charts can significantly enhance the clarity and impact of your message.
One of the key challenges associated with charting is choosing the right chart type for your data and purpose. Using the wrong chart can misrepresent information or make it difficult to understand. For example, using a pie chart to represent data with too many categories can lead to a cluttered and confusing visual. Similarly, using a line chart to display data that isn't sequential can be misleading. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different chart types is essential for effective data visualization.
A simple bar chart is a great example of a commonly used chart type. It uses rectangular bars to represent data, with the height of each bar corresponding to the value it represents. This type of chart is ideal for comparing different categories or tracking changes over time. Another example is a line chart, which connects data points with lines to show trends and patterns over a continuous period.
Three key benefits of using charts are clarity, engagement, and memorability. Charts clarify complex information by presenting it visually, making it easier for the audience to understand patterns and relationships within the data. Visually appealing charts are more engaging than raw data, capturing the audience's attention and making the information more interesting. Furthermore, information presented visually is more likely to be remembered than information presented solely in text form.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Charts
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clarity | Potential for Misinterpretation |
| Engagement | Can Oversimplify Complex Data |
| Memorability | Requires Careful Design |
Five best practices for implementing charts include choosing the right chart type, keeping it simple, using clear labels, ensuring accessibility, and providing context.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a chart? - A visual representation of data.
2. Why are charts important? - They enhance understanding of data.
3. What are different types of charts? - Bar charts, line charts, pie charts, etc.
4. How do I choose the right chart? - Consider your data and purpose.
5. What are some common charting mistakes? - Using the wrong chart type, cluttered design.
6. How can I make my charts accessible? - Use clear labels and alt text.
7. What are some good resources for learning about charts? - Data visualization books and online tutorials.
8. Where can I find charting software? - Many online tools and software packages offer charting capabilities.
Tips and tricks for creating effective charts include using contrasting colors, avoiding 3D effects unless necessary, and keeping the design clean and uncluttered. Consider your audience and tailor the chart to their level of understanding.
In conclusion, charts offer a powerful way to transform complex data into meaningful insights. From simplifying complex information to engaging audiences and aiding memorability, the benefits of effective charting are numerous. By understanding the different chart types, following best practices, and addressing potential challenges, we can harness the power of charts to communicate data effectively and make informed decisions. Embracing visual communication through charts will undoubtedly enhance your ability to share information, tell compelling stories with data, and unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us. So, next time you're faced with a mountain of data, remember the power of the chart – it's your key to unlocking clarity, insight, and impactful communication. Start exploring the world of charts today and discover the transformative potential they hold for your work and understanding.
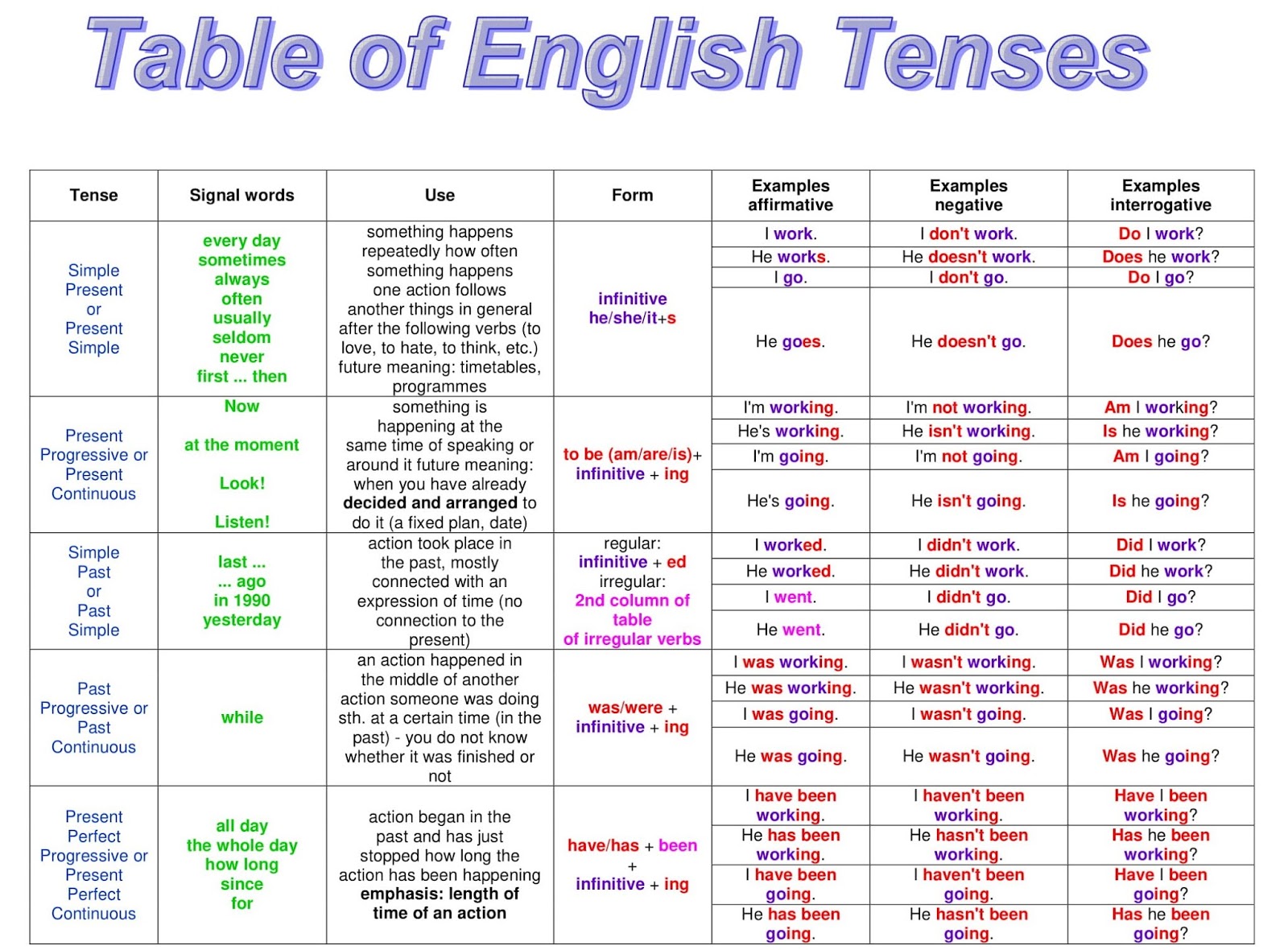
English Tense Chart With Rules And Examples Pdf - Trees By Bike
How To Pronounce R Sound In American English at Candida Adkins blog - Trees By Bike
EPA Vowel Color Chart - Trees By Bike
The Most Widely Spoken Language In The World - Trees By Bike
Timeline Infographic Infographic Marketing Inbound Marketing - Trees By Bike
Enabling the Display Size Comparison Chart - Trees By Bike
Hangul Consonants And Vowels Chart Phonetics Sounds Ppt - Trees By Bike
English as a Second Language Welcome - Trees By Bike
Pin on Vintage paper - Trees By Bike
Writing about a pie chart - Trees By Bike
Free Printable Adjective Chart - Trees By Bike
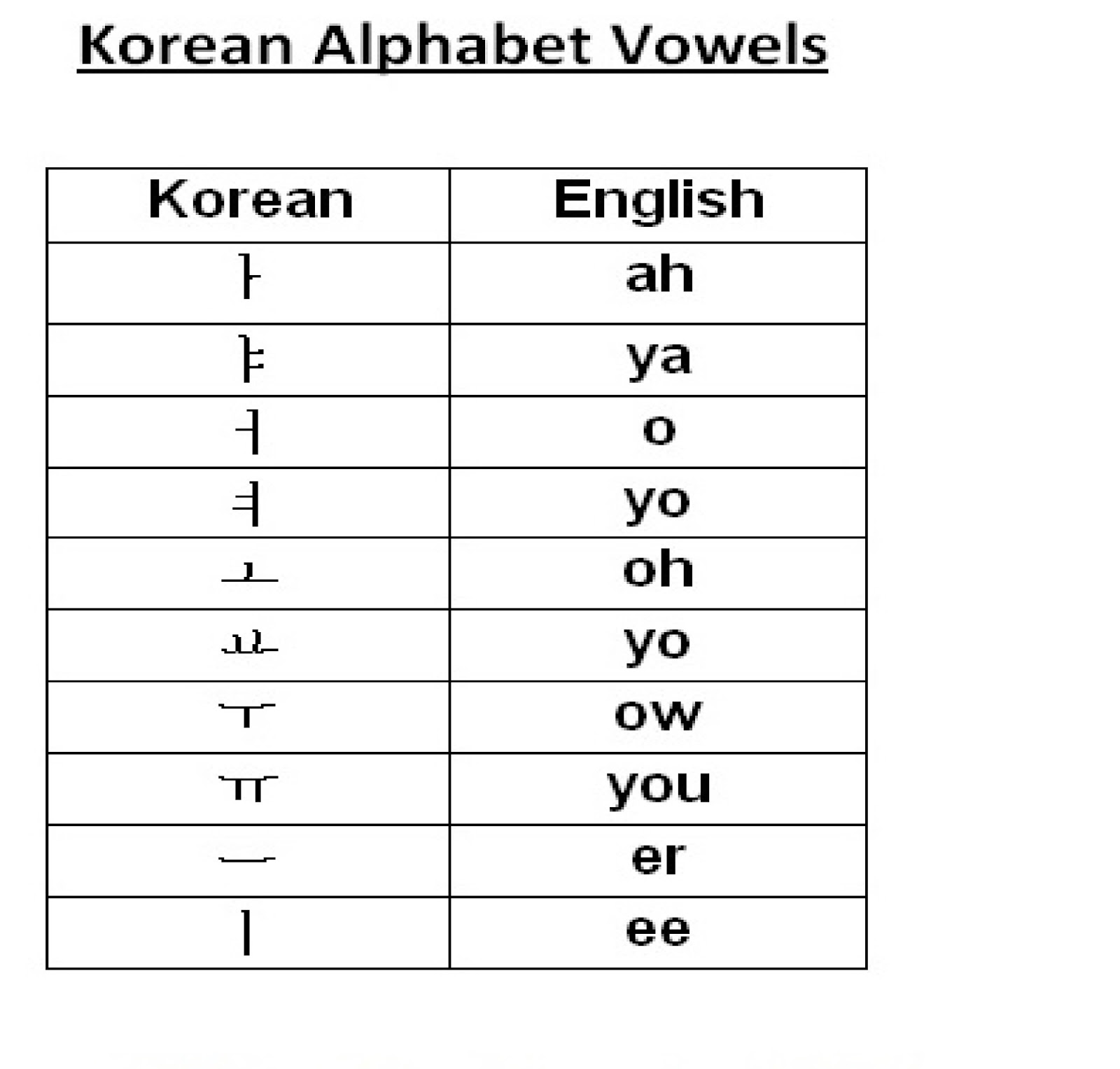
Korean Consonants And Vowels Chart Kindergarten Game - Trees By Bike
chart in english language - Trees By Bike
Grab pares losses by 24 deliveries unit breaks even ahead of target - Trees By Bike
Hooded Eye Makeup Tutorial Face Chart Makeup Studio Eye Makeup Art - Trees By Bike