Imagine holding a miniature version of the world in your hands, a tool that lets you traverse vast distances and explore unfamiliar terrains from the comfort of your home. This is the power of maps, and at the heart of their functionality lies a crucial concept: map scale. Understanding how to determine map scale is like unlocking a secret code, revealing the true proportions of the world represented on that piece of paper.
But why is this seemingly technical detail so important? Imagine planning a hiking trip using a map without understanding its scale. You might misjudge distances, leading to inaccurate estimations of travel time and potentially jeopardizing your journey. Determining map scale allows us to accurately measure distances, estimate travel times, and gain a true sense of the spatial relationships between different locations.
The concept of map scale has been around for centuries, evolving alongside cartography itself. Early maps relied on simple ratios and verbal descriptions to convey scale. As mapmaking techniques advanced, so too did the methods for representing scale, leading to the standardized systems we use today. Despite these advancements, challenges remain in accurately representing a three-dimensional world on a two-dimensional surface, highlighting the ongoing importance of understanding and interpreting map scale.
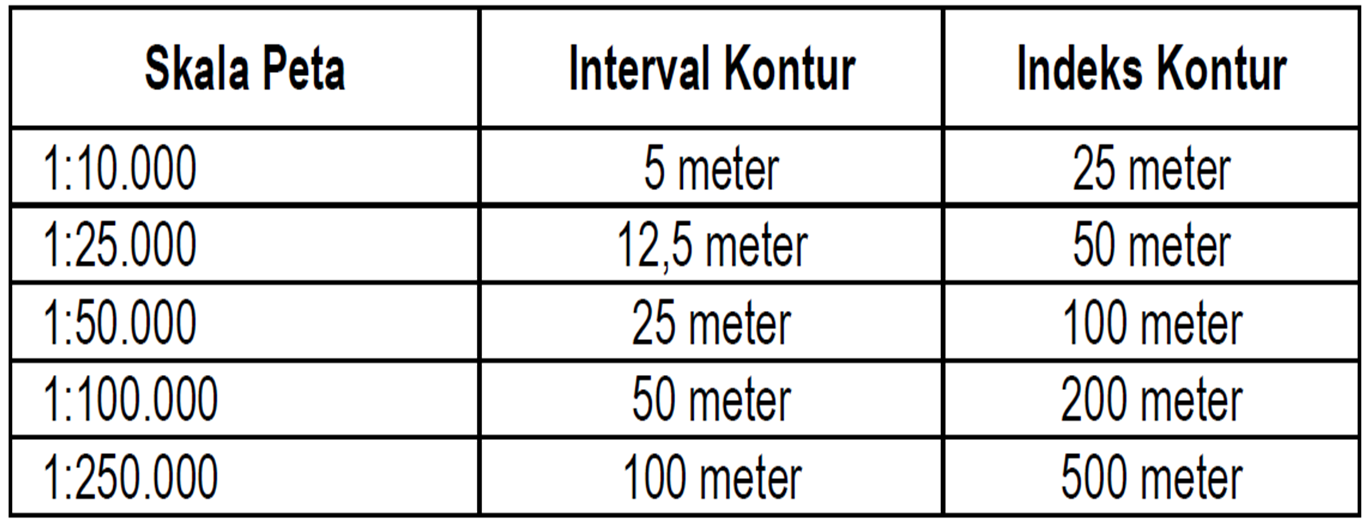
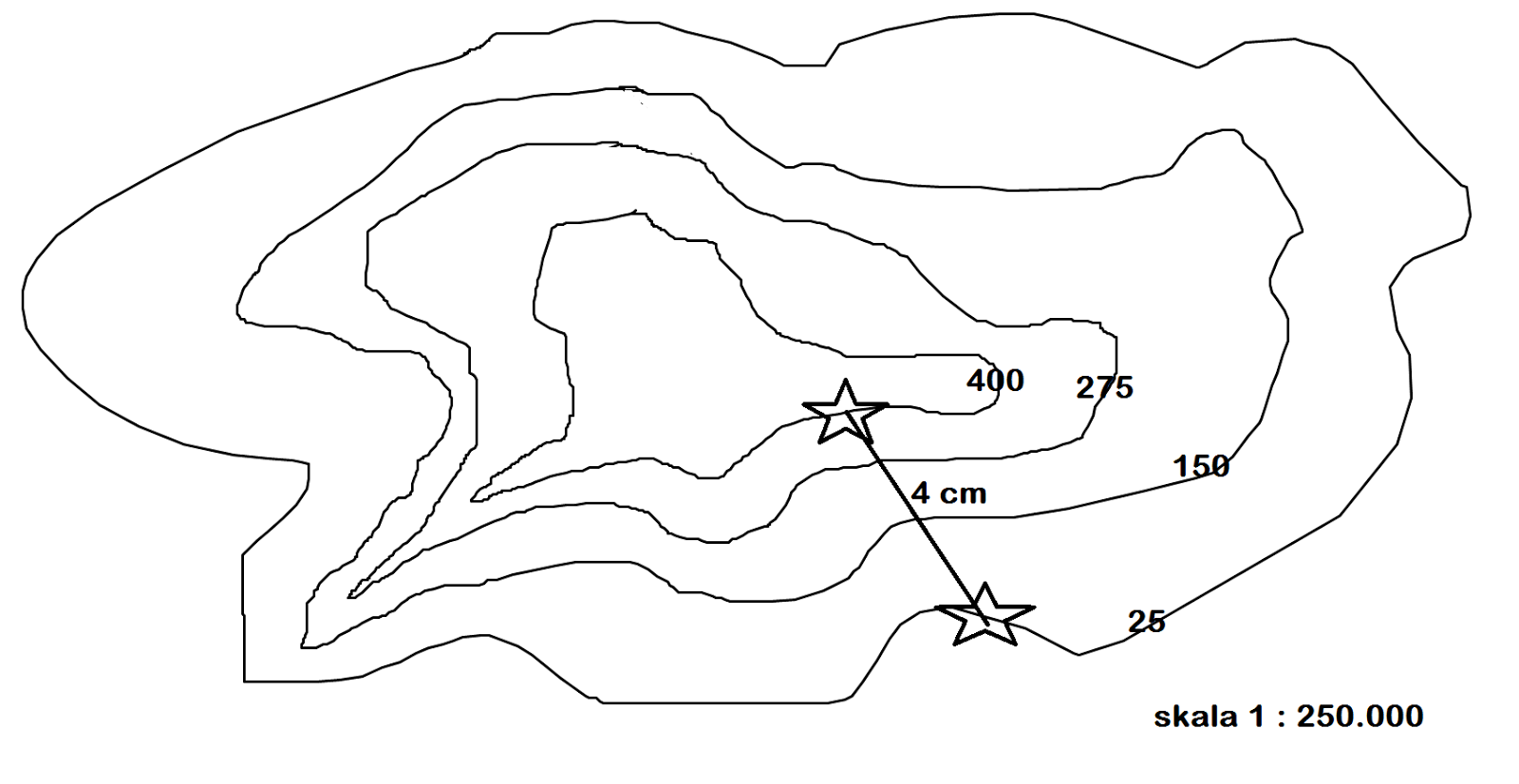
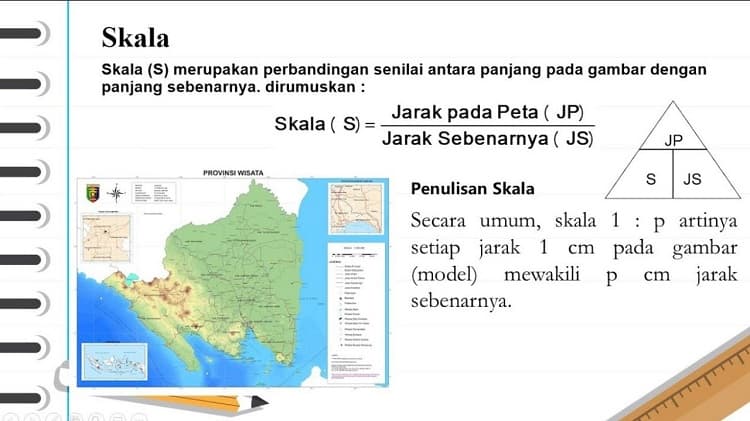
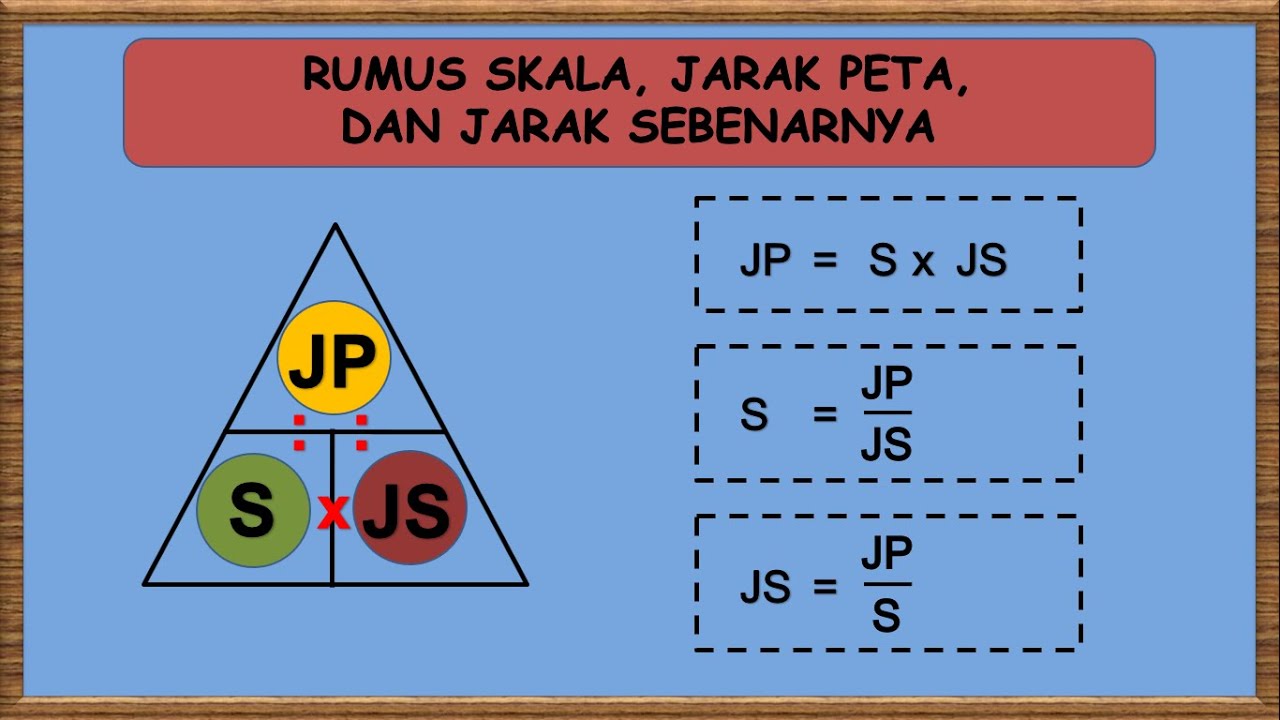
Determining map scale is essentially about understanding the relationship between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This relationship is typically expressed in one of three ways: as a ratio (e.g., 1:50,000), a verbal statement (e.g., "1 centimeter equals 500 meters"), or a graphic scale (a bar with markings representing specific distances).
Each method of representing scale offers its own advantages. The ratio provides a concise and universally understood representation. The verbal statement offers a more intuitive understanding, particularly for those unfamiliar with map ratios. The graphic scale provides a quick visual reference, allowing users to measure distances directly on the map. Regardless of the method used, the fundamental principle remains the same: to translate the miniaturized world of the map back to the real-world distances we experience.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Map Scale Representations
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Ratio (e.g., 1:50,000) | Concise, universally understood, easily comparable across maps | May not be intuitive for all users |
| Verbal Statement (e.g., "1 centimeter equals 500 meters") | Easy to understand, directly relates map distance to real-world distance | Can be cumbersome for very large or very small scales |
| Graphic Scale (bar with distance markings) | Provides a quick visual reference, allows for direct measurement on the map | Accuracy can be affected by resizing or printing issues |
Understanding map scale is crucial for anyone who uses maps, from hikers and travelers to city planners and geographers. By accurately interpreting map scales, we can navigate our world with greater confidence, make informed decisions based on spatial relationships, and appreciate the vastness and complexity of the world around us.
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike
cara menentukan skala peta - Trees By Bike