Ever wondered how engineers visualize the intricate dance of currents and voltages within a three-phase induction motor? The answer lies in the elegant power of phasor diagrams. These graphical representations provide a crucial window into the motor's internal workings, allowing us to understand its performance characteristics and diagnose potential issues.
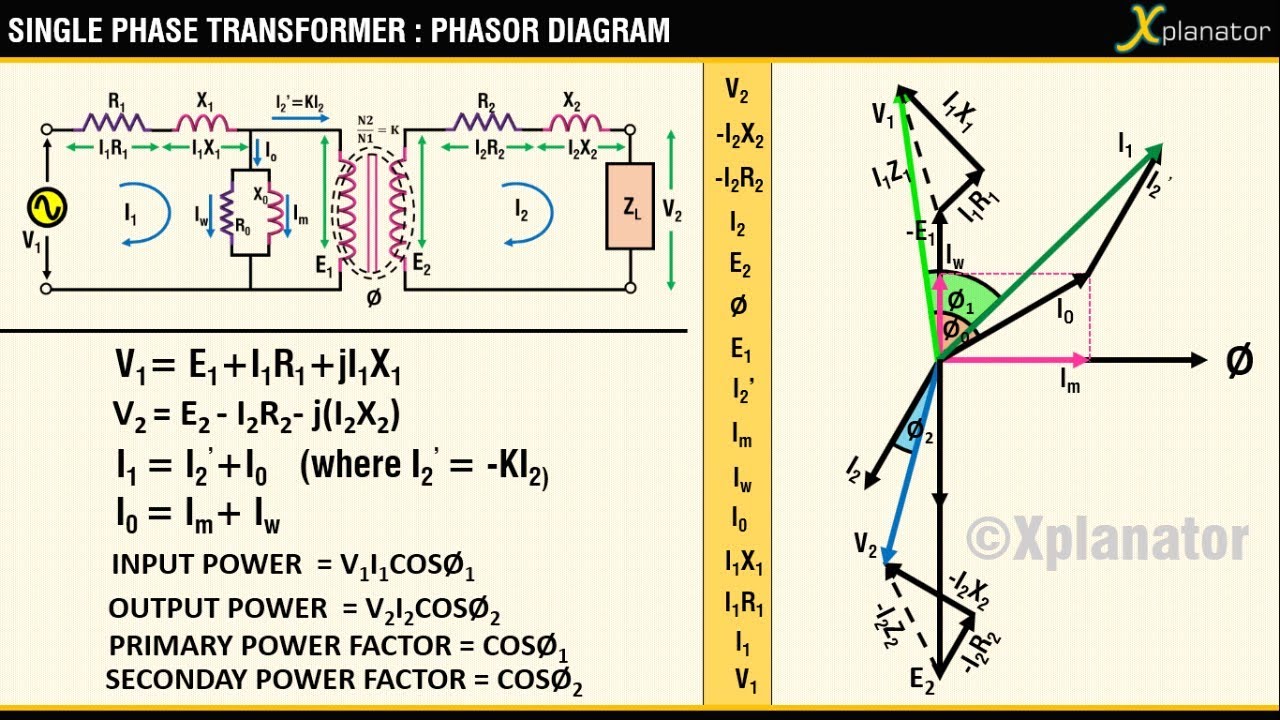
A phasor diagram for a three-phase induction motor is essentially a snapshot of the relationship between the various electrical quantities at play within the motor at a specific moment in time. It depicts voltages, currents, and magnetic fluxes as rotating vectors, or phasors, with their lengths representing magnitude and their angles representing phase difference. By analyzing these diagrams, we can gain valuable insights into the motor's operating conditions.
The concept of phasor representation emerged from the need to simplify the analysis of alternating current (AC) circuits. Early electrical engineers grappled with complex mathematical equations to describe the sinusoidal nature of AC waveforms. Phasors provided a visual and intuitive alternative, making it easier to understand the interactions of voltages and currents in AC systems, including three-phase induction motors, which became the workhorse of industrial applications.
The significance of phasor diagrams in the context of three-phase induction motors cannot be overstated. They are indispensable for understanding how factors like load, speed, and power factor influence the motor's behavior. A well-constructed phasor diagram can reveal whether the motor is operating efficiently or if adjustments are needed to optimize its performance. One common issue addressed using phasor diagrams is the analysis of motor starting conditions, where high inrush currents can be a concern.
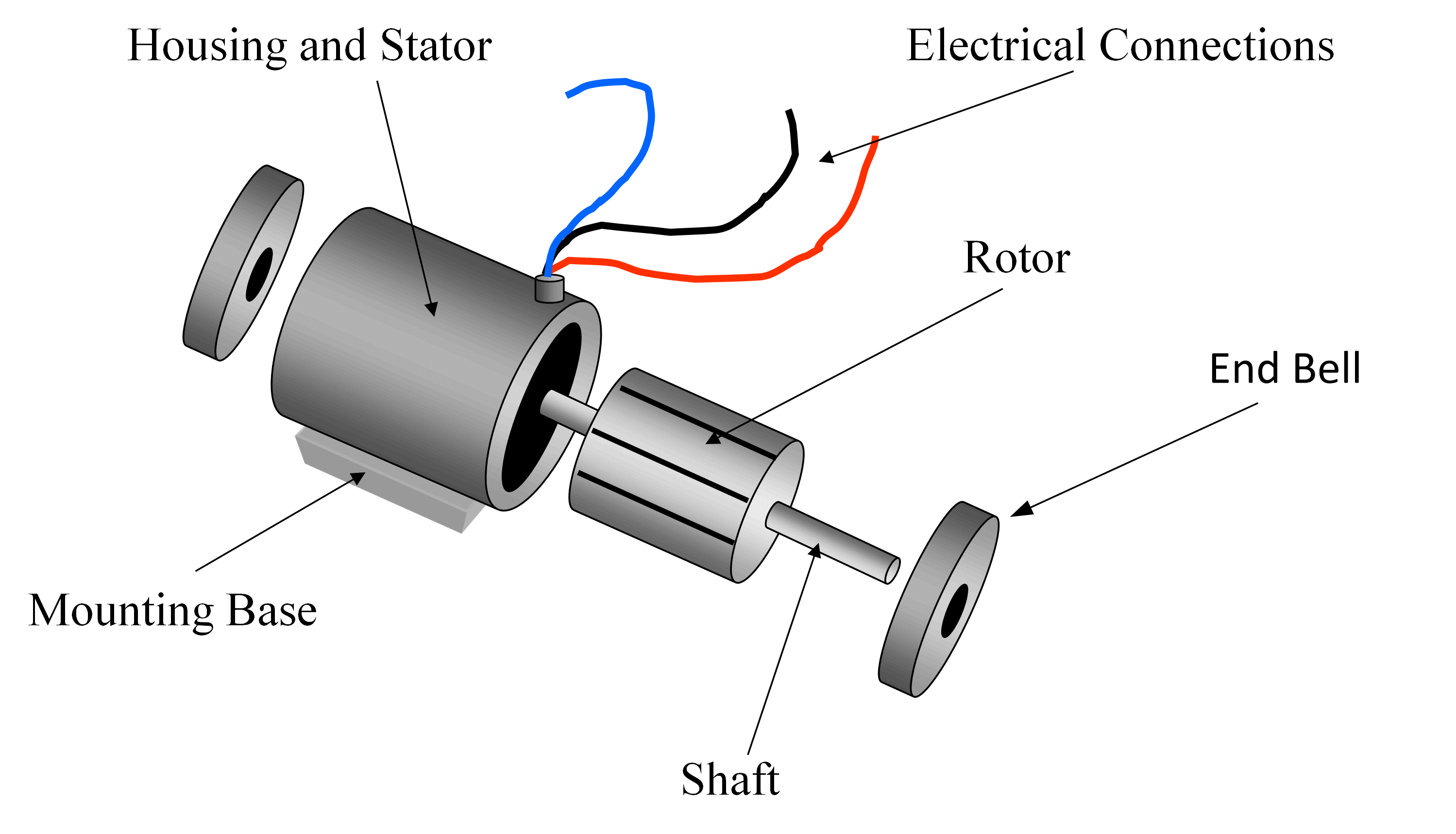
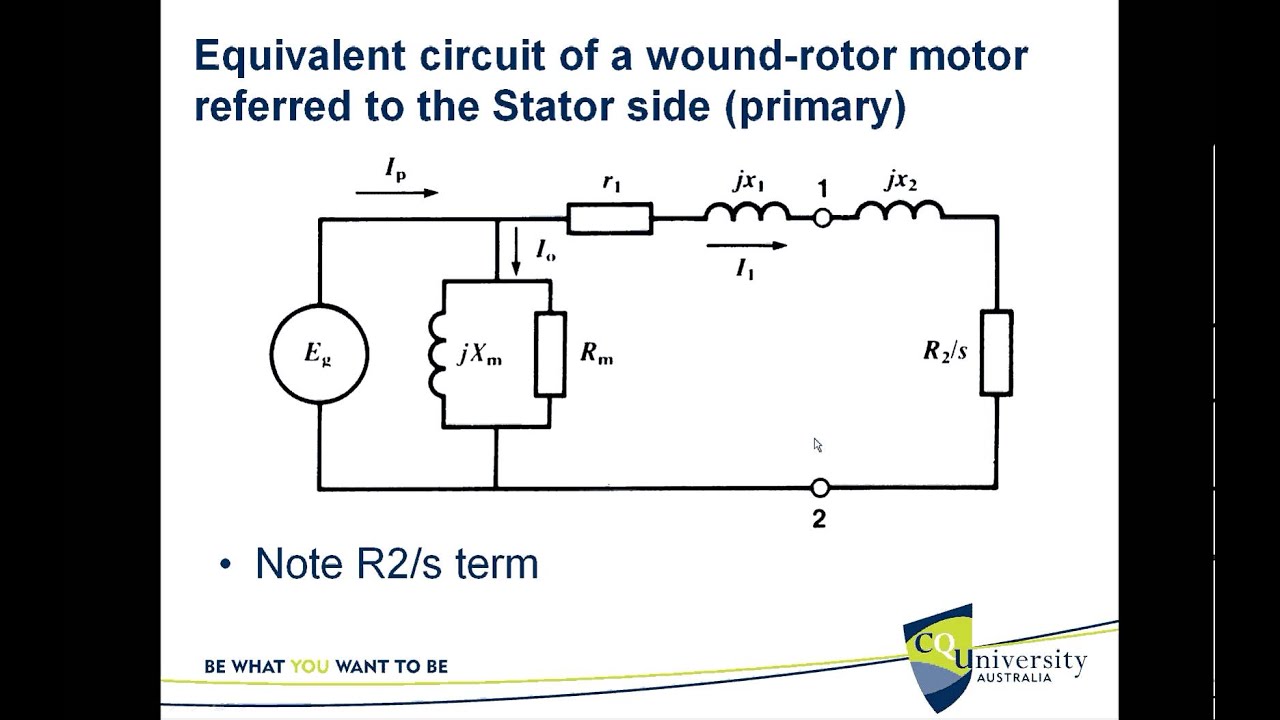
Let's delve deeper into the construction of a basic three-phase induction motor phasor diagram. The stator's three-phase windings produce a rotating magnetic field. This rotating field induces voltages in the rotor windings, resulting in rotor currents. These rotor currents, in turn, create a magnetic field that interacts with the stator's rotating field, producing torque and causing the motor to rotate. The phasor diagram visually represents these interactions by showing the phase relationships between the stator voltage, stator current, rotor current, and the induced electromotive force (EMF) in the rotor.
Three key benefits of using three-phase induction motor graphical vector representations are: Simplified Analysis: They simplify complex AC circuit analysis. Performance Prediction: They enable prediction of motor performance under varying loads. Troubleshooting: They aid in diagnosing motor faults and inefficiencies.
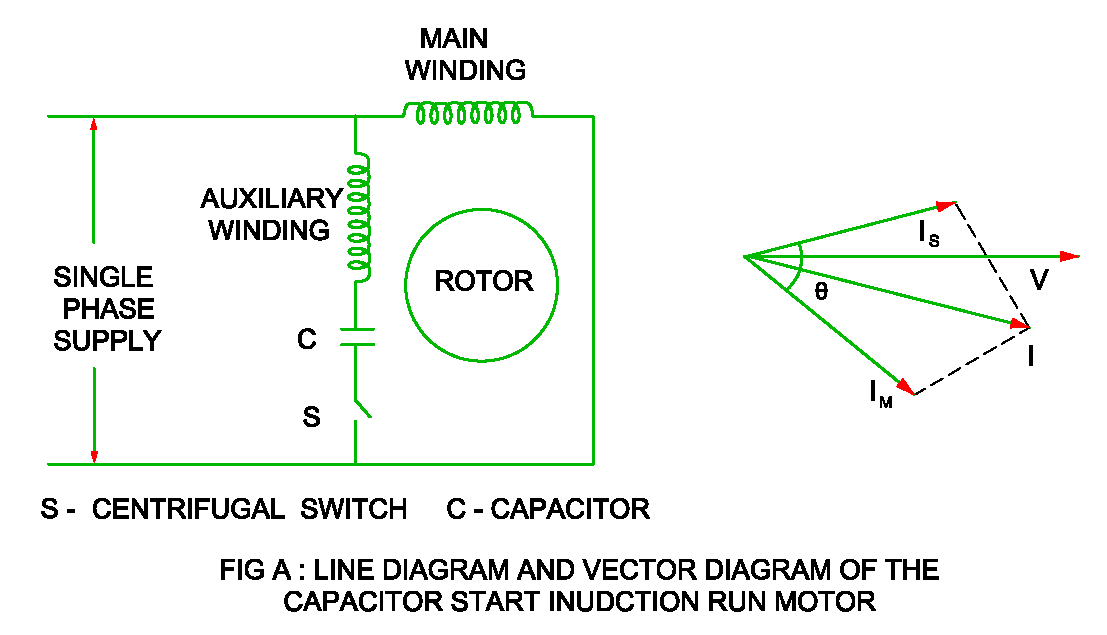
To construct a diagram, start by drawing the stator voltage phasors. Then, based on the motor's equivalent circuit parameters, determine the stator current phasor and its angle relative to the voltage. Next, represent the rotor induced EMF and rotor current phasors, considering the slip (the difference between synchronous speed and rotor speed). Finally, depict the air-gap flux phasor, which links the stator and rotor magnetic fields.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Utilizing Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Visual representation simplifies complex relationships | Can be complex to construct for advanced motor models |
| Facilitates understanding of motor performance | Provide a steady-state view, not transient behavior |
| Aids in troubleshooting and optimization | Require understanding of underlying electrical principles |
Best Practices: 1. Understand the equivalent circuit of the motor. 2. Accurately represent the phase relationships between different phasors. 3. Use appropriate scaling for magnitudes. 4. Clearly label all phasors and angles. 5. Consider the effects of load and slip.
Real Examples: Phasor diagrams are used to analyze motor performance under different load conditions, assess the impact of power factor correction, evaluate the effects of voltage variations, and investigate the causes of motor overheating and design control strategies for variable speed drives.
Challenges and Solutions: Dealing with complex motor models can be simplified by using software tools. Difficulty in visualizing three-dimensional phasor relationships can be overcome by using interactive simulations.
FAQs: 1. What is a phasor? 2. How is slip represented? 3. What is the significance of the power factor angle? 4. How do phasor diagrams help in motor control? 5. What are the limitations of phasor diagrams? 6. How do you analyze a phasor diagram for a faulty motor? 7. What software tools are available for creating phasor diagrams? 8. How can I learn more about phasor analysis?
Tips and Tricks: Utilize software for complex scenarios. Start with simplified diagrams. Practice interpreting diagrams for various operating conditions. Focus on understanding the key relationships between voltage, current, and flux.
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are an essential tool for anyone working with three-phase induction motors. They provide a visual and intuitive way to understand the complex interactions of electrical quantities within the motor. From simplifying analysis and predicting performance to troubleshooting issues and optimizing design, the applications of phasor diagrams are vast. By mastering the art of interpreting these diagrams, engineers and technicians can gain valuable insights into motor behavior and ensure efficient and reliable operation. Exploring resources like textbooks, online tutorials, and simulation software can further enhance your understanding and ability to apply this powerful technique effectively. This knowledge is crucial for improving motor efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing the overall performance of industrial systems that rely heavily on these workhorse machines. Invest the time to deeply understand this concept and unlock a new level of control over your motor applications.
phasor diagram of three phase induction motor - Trees By Bike
Can You Slow Down An Electric Motor at Walter Stone blog - Trees By Bike
Start And Run Capacitors For Electric Motors - Trees By Bike
phasor diagram of three phase induction motor - Trees By Bike
Induction Motor Phasor Diagram - Trees By Bike
3 Phase Delta Motor Wiring Diagram - Trees By Bike
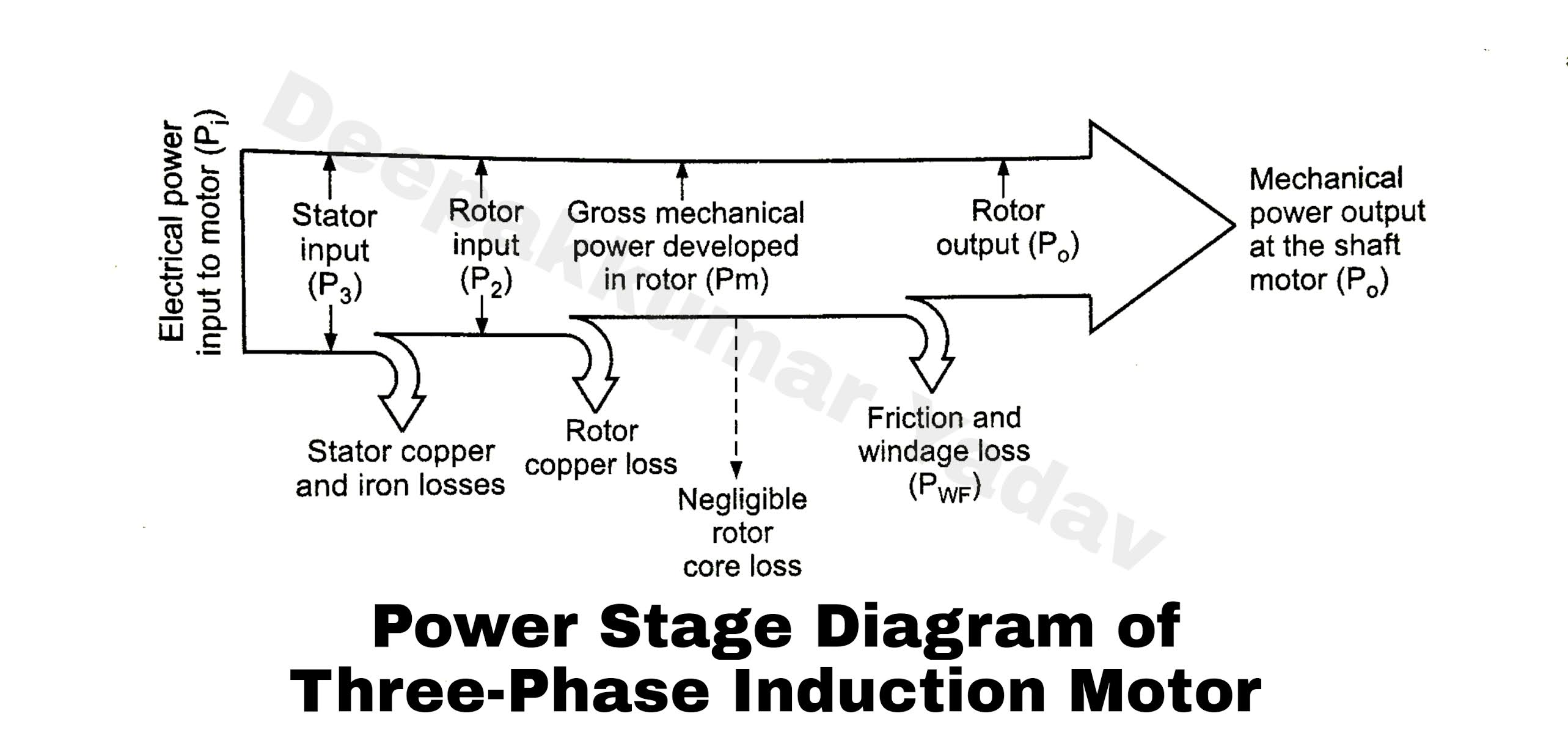
Energy Flow Diagram of Induction Motor - Trees By Bike
Three Phase Induction Motors - Trees By Bike
Basic Phasor Diagram Electric Circuit - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagrams Of Ac Circuits - Trees By Bike
DIAGRAM Wiring Diagram Of Three Phase Induction Motor - Trees By Bike
Inductive Circuit Phasor Diagram - Trees By Bike
phasor diagram of three phase induction motor - Trees By Bike
Split Phase Induction Motor - Trees By Bike
Phasor Diagram Of Three Phase Induction Motor - Trees By Bike